Amyloid-PET predicts inhibition of de novo plaque formation upon chronic γ-secretase modulator treatment
- PMID: 26055427
- PMCID: PMC4759098
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2015.74
Amyloid-PET predicts inhibition of de novo plaque formation upon chronic γ-secretase modulator treatment
Abstract
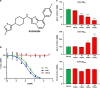
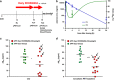
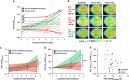
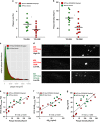
In a positron-emission tomography (PET) study with the β-amyloid (Aβ) tracer [(18)F]-florbetaben, we previously showed that Aβ deposition in transgenic mice expressing Swedish mutant APP (APP-Swe) mice can be tracked in vivo. γ-Secretase modulators (GSMs) are promising therapeutic agents by reducing generation of the aggregation prone Aβ42 species without blocking general γ-secretase activity. We now aimed to investigate the effects of a novel GSM [8-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-2-yl]-[1-(3-methyl-[1,2,4]thiadiazol-5-yl)-piperidin-4-yl]-amine (RO5506284) displaying high potency in vitro and in vivo on amyloid plaque burden and used longitudinal Aβ-microPET to trace individual animals. Female transgenic (TG) APP-Swe mice aged 12 months (m) were assigned to vehicle (TG-VEH, n=12) and treatment groups (TG-GSM, n=12), which received daily RO5506284 (30 mg kg(-1)) treatment for 6 months. A total of 131 Aβ-PET recordings were acquired at baseline (12 months), follow-up 1 (16 months) and follow-up 2 (18 months, termination scan), whereupon histological and biochemical analyses of Aβ were performed. We analyzed the PET data as VOI-based cortical standard-uptake-value ratios (SUVR), using cerebellum as reference region. Individual plaque load assessed by PET remained nearly constant in the TG-GSM group during 6 months of RO5506284 treatment, whereas it increased progressively in the TG-VEH group. Baseline SUVR in TG-GSM mice correlated with Δ%-SUVR, indicating individual response prediction. Insoluble Aβ42 was reduced by 56% in the TG-GSM versus the TG-VEH group relative to the individual baseline plaque load estimates. Furthermore, plaque size histograms showed differing distribution between groups of TG mice, with fewer small plaques in TG-GSM animals. Taken together, in the first Aβ-PET study monitoring prolonged treatment with a potent GSM in an AD mouse model, we found clear attenuation of de novo amyloidogenesis. Moreover, longitudinal PET allows non-invasive assessment of individual plaque-load kinetics, thereby accommodating inter-animal variations.
Conflict of interest statement
CH is an advisor of F. Hoffmann-La Roche. JB, TL and KB are employees of F. Hoffmann-La Roche. PB and AR have received speaking honoraria from Piramal Imaging. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- 1Ziegler-Graham K, Brookmeyer R, Johnson E, Arrighi HM. Worldwide variation in the doubling time of Alzheimer's disease incidence rates. Alzheimers Dement 2008; 4: 316–323. - PubMed
-
- 2Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol 1991; 82: 239–259. - PubMed
-
- 3Haass C, Selkoe DJ. Soluble protein oligomers in neurodegeneration: lessons from the Alzheimer's amyloid beta-peptide. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007; 8: 101–112. - PubMed
-
- 4Sun X, Jin L, Ling P. Review of drugs for Alzheimer's disease. Drug Discov Ther 2012; 6: 285–290. - PubMed
-
- 5Reisberg B, Doody R, Stoffler A, Schmitt F, Ferris S, Mobius HJ. Memantine in moderate-to-severe Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 1333–1341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

