Changes in ventricular remodelling and clinical status during the year following a single administration of stromal cell-derived factor-1 non-viral gene therapy in chronic ischaemic heart failure patients: the STOP-HF randomized Phase II trial
- PMID: 26056125
- PMCID: PMC4554960
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv254
Changes in ventricular remodelling and clinical status during the year following a single administration of stromal cell-derived factor-1 non-viral gene therapy in chronic ischaemic heart failure patients: the STOP-HF randomized Phase II trial
Abstract
Background: Stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) promotes tissue repair through mechanisms of cell survival, endogenous stem cell recruitment, and vasculogenesis. Stromal Cell-Derived Factor-1 Plasmid Treatment for Patients with Heart Failure (STOP-HF) is a Phase II, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial to evaluate safety and efficacy of a single treatment of plasmid stromal cell-derived factor-1 (pSDF-1) delivered via endomyocardial injection to patients with ischaemic heart failure (IHF).
Methods: Ninety-three subjects with IHF on stable guideline-based medical therapy and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) ≤40%, completed Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire (MLWHFQ) and 6-min walk distance (6 MWD), were randomized 1 : 1 : 1 to receive a single treatment of either a 15 or 30 mg dose of pSDF-1 or placebo via endomyocardial injections. Safety and efficacy parameters were assessed at 4 and 12 months after injection. Left ventricular functional and structural measures were assessed by contrast echocardiography and quantified by a blinded independent core laboratory. Stromal Cell-Derived Factor-1 Plasmid Treatment for Patients with Heart Failure was powered based on change in 6 MWD and MLWHFQ at 4 months.
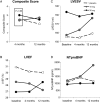
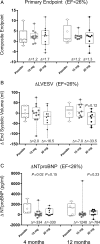
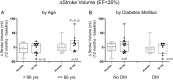
Results: Subject profiles at baseline were (mean ± SD): age 65 ± 9 years, LVEF 28 ± 7%, left ventricular end-systolic volume (LVESV) 167 ± 66 mL, N-terminal pro brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) (NTproBNP) 1120 ± 1084 pg/mL, MLWHFQ 50 ± 20 points, and 6 MWD 289 ± 99 m. Patients were 11 ± 9 years post most recent myocardial infarction. Study injections were delivered without serious adverse events in all subjects. Sixty-two patients received drug with no unanticipated serious product-related adverse events. The primary endpoint was a composite of change in 6 MWD and MLWHFQ from baseline to 4 months follow-up. The primary endpoint was not met (P = 0.89). For the patients treated with pSDF-1, there was a trend toward an improvement in LVEF at 12 months (placebo vs. 15 mg vs. 30 mg ΔLVEF: -2 vs. -0.5 vs. 1.5%, P = 0.20). A pre-specified analysis of the effects of pSDF-1 based on tertiles of LVEF at entry revealed improvements in EF and LVESV from lowest-to-highest LVEF. Patients in the first tertile of EF (<26%) that received 30 mg of pSDF-1 demonstrated a 7% increase in EF compared with a 4% decrease in placebo (ΔLVEF = 11%, P = 0.01) at 12 months. There was also a trend towards improvement in LVESV, with treated patients demonstrating an 18.5 mL decrease compared with a 15 mL increase for placebo at 12 months (ΔLVESV = 33.5 mL, P = 0.12). The change in end-diastolic and end-systolic volume equated to a 14 mL increase in stroke volume in the patients treated with 30 mg of pSDF-1 compared with a decrease of -11 mL in the placebo group (ΔSV = 25 mL, P = 0.09). In addition, the 30 mg-treated cohort exhibited a trend towards improvement in NTproBNP compared with placebo at 12 months (-784 pg/mL, P = 0.23).
Conclusions: The blinded placebo-controlled STOP-HF trial demonstrated the safety of a single endocardial administration of pSDF-1 but failed to demonstrate its primary endpoint of improved composite score at 4 months after treatment. Through a pre-specified analysis the STOP-HF trial demonstrates the potential for attenuating LV remodelling and improving EF in high-risk ischaemic cardiomyopathy. The safety profile supports repeat dosing with pSDF-1 and the degree of left ventricular remodelling suggests the potential for improved outcomes in larger future trials.
Keywords: Chronic heart failure; Endogenous tissue repair; Gene therapy; Stem cell homing.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures


Comment in
-
It is never too late for native cardiac repair: can genes awake the Sleeping Beauty in chronic patients?Eur Heart J. 2015 Sep 1;36(33):2207-9. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv258. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Eur Heart J. 2015. PMID: 26071429 No abstract available.
-
Gene therapy: Can SDF-1 improve cardiac function?Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015 Aug;12(8):442. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2015.103. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 26122024 No abstract available.
References
-
- Askari A, Unzek S, Popovic ZB, Goldman CK, Forudi F, Kiedrowski M, Rovner A, Ellis SG, Thomas JD, DiCorleto PE, Topol EJ, Penn MS. Effect of stromal-cell-derived factor-1 on stem cell homing and tissue regeneration in ischemic cardiomyopathy. Lancet 2003;362:697–703. - PubMed
-
- Deglurkar I, Mal N, Mills WR, Popovic ZB, McCarthy P, Blackstone EH, Laurita KR, Penn MS. Mechanical and electrical effects of cell-based gene therapy for ischemic cardiomyopathy are independent. Hum Gene Ther 2006;17:1144–1151. - PubMed
-
- Unzek S, Zhang M, Mal N, Mills WR, Laurita KR, Penn MS. SDF-1 recruits cardiac stem cell like cells that depolarize in vivo. Cell Transplant 2007;16:879–886. - PubMed
-
- Yamaguchi J, Kusano KF, Masuo O, Kawamoto A, Silver M, Murasawa S, Bosch-Marce M, Masuda H, Losordo DW, Isner JM, Asahara T. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 effects on ex vivo expanded endothelial progenitor cell recruitment for ischemic neovascularization. Circulation 2003;107:1322–1328. - PubMed
-
- Zhang M, Mal N, Kiedrowski M, Chacko M, Askari AT, Popovic ZB, Koc ON, Penn MS. SDF-1 expression by mesenchymal stem cells results in trophic support of cardiac myocytes after myocardial infarction. FASEB J 2007;21:3197–3207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

