Contingency and entrenchment in protein evolution under purifying selection
- PMID: 26056312
- PMCID: PMC4485141
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1412933112
Contingency and entrenchment in protein evolution under purifying selection
Abstract
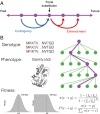
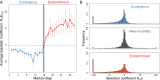
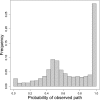
The phenotypic effect of an allele at one genetic site may depend on alleles at other sites, a phenomenon known as epistasis. Epistasis can profoundly influence the process of evolution in populations and shape the patterns of protein divergence across species. Whereas epistasis between adaptive substitutions has been studied extensively, relatively little is known about epistasis under purifying selection. Here we use computational models of thermodynamic stability in a ligand-binding protein to explore the structure of epistasis in simulations of protein sequence evolution. Even though the predicted effects on stability of random mutations are almost completely additive, the mutations that fix under purifying selection are enriched for epistasis. In particular, the mutations that fix are contingent on previous substitutions: Although nearly neutral at their time of fixation, these mutations would be deleterious in the absence of preceding substitutions. Conversely, substitutions under purifying selection are subsequently entrenched by epistasis with later substitutions: They become increasingly deleterious to revert over time. Our results imply that, even under purifying selection, protein sequence evolution is often contingent on history and so it cannot be predicted by the phenotypic effects of mutations assayed in the ancestral background.
Keywords: coevolution; intragenic epistasis; near neutrality; protein stability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Weinreich DM, Delaney NF, Depristo MA, Hartl DL. Darwinian evolution can follow only very few mutational paths to fitter proteins. Science. 2006;312(5770):111–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

