Correlation of Carotid Intraplaque Hemorrhage and Stroke Using 1.5 T and 3 T MRI
- PMID: 26056469
- PMCID: PMC4454204
- DOI: 10.4137/MRI.S23560
Correlation of Carotid Intraplaque Hemorrhage and Stroke Using 1.5 T and 3 T MRI
Abstract
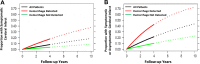
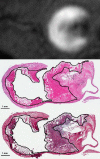
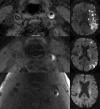
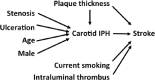
Carotid therosclerotic disease causes approximately 25% of the nearly 690,000 ischemic strokes each year in the United States. Current risk stratification based on percent stenosis does not provide specific information on the actual risk of stroke for most individuals. Prospective randomized studies have found only 10 to 12% of asymptomatic patients will have a symptomatic stroke within 5 years. Measurements of percent stenosis do not determine plaque stability or composition. Reports have concluded that cerebral ischemic events associated with carotid plaque are intimately associated with plaque instability. Analysis of retrospective studies has found that plaque composition is important in risk stratification. Only MRI has the ability to identify and measure the detailed components and morphology of carotid plaque and provides more detailed information than other currently available techniques. MRI can accurately detect carotid hemorrhage, and MRI identified carotid hemorrhage correlates with acute stroke.
Keywords: MRI; carotid; hemorrhage.
Figures

References
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ, Brown TM, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2010 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010;121(7):e46–e215. - PubMed
-
- McPhee JT, Schanzer A, Messina LM, Eslami MH. Carotid artery stenting has increased rates of postprocedure stroke, death, and resource utilization than does carotid endarterectomy in the United States, 2005. J Vasc Surg. 2008;48(6):1442–1450. 1450 e1441. - PubMed
-
- Carotid surgery versus medical therapy in asymptomatic carotid stenosis. The CASANOVA Study Group. Stroke. 1991;22(10):1229–1235. - PubMed
-
- Endarterectomy for asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis. Executive Committee for the Asymptomatic Carotid Atherosclerosis Study. JAMA. 1995;273(18):1421–1428. - PubMed
-
- Risk of stroke in the distribution of an asymptomatic carotid artery. The European Carotid Surgery Trialists Collaborative Group. Lancet. 1995;345(8944):209–212. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

