Network-Based Analysis on Orthogonal Separation of Human Plasma Uncovers Distinct High Density Lipoprotein Complexes
- PMID: 26057100
- PMCID: PMC6524531
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00419
Network-Based Analysis on Orthogonal Separation of Human Plasma Uncovers Distinct High Density Lipoprotein Complexes
Abstract
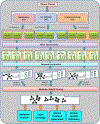
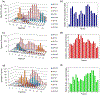
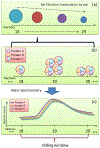
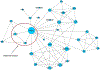
High density lipoprotein (HDL) particles are blood-borne complexes whose plasma levels have been associated with protection from cardiovascular disease (CVD). Recent studies have demonstrated the existence of distinct HDL subspecies; however, these have been difficult to isolate and characterize biochemically. Here, we present the first report that employs a network-based approach to systematically infer HDL subspecies. Healthy human plasma was separated into 58 fractions using our previously published three orthogonal chromatography techniques. Similar local migration patterns among HDL proteins were captured with a novel similarity score, and individual comigration networks were constructed for each fraction. By employing a graph mining algorithm, we identified 183 overlapped cliques, among which 38 were further selected as candidate HDL subparticles. Each of these 38 subparticles had at least two literature supports. In addition, GO function enrichment analysis showed that they were enriched with fundamental biological and CVD protective functions. Furthermore, gene knockout experiments in mouse model supported the validity of these subparticles related to three apolipoproteins. Finally, analysis of an apoA-I deficient human patient's plasma provided additional support for apoA-I related complexes. Further biochemical characterization of these putative subspecies may facilitate the mechanistic research of CVD and guide targeted therapeutics aimed at its mitigation.
Keywords: apolipoprotein; comigration pattern; high-density lipoprotein; human plasma; maximal clique; particle fractionation; protein network; proteomics; subspecies.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mapping Atheroprotective Functions and Related Proteins/Lipoproteins in Size Fractionated Human Plasma.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2017 Apr;16(4):680-693. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M116.066290. Epub 2017 Feb 21. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28223350 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-dimensional co-separation analysis reveals protein-protein interactions defining plasma lipoprotein subspecies.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013 Nov;12(11):3123-34. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M113.028134. Epub 2013 Jul 23. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23882025 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of genetic deletion of platform apolipoproteins on the size distribution of the murine lipoproteome.J Proteomics. 2016 Sep 2;146:184-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2016.06.035. Epub 2016 Jul 3. J Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 27385375 Free PMC article.
-
The Difference Between High Density Lipoprotein Subfractions and Subspecies: an Evolving Model in Cardiovascular Disease and Diabetes.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2021 Mar 27;23(6):23. doi: 10.1007/s11883-021-00925-4. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2021. PMID: 33772657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomic Study Makes High-Density Lipoprotein a Biomarker for Atherosclerotic Vascular Disease.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:164846. doi: 10.1155/2015/164846. Epub 2015 May 18. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26090384 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mapping Atheroprotective Functions and Related Proteins/Lipoproteins in Size Fractionated Human Plasma.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2017 Apr;16(4):680-693. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M116.066290. Epub 2017 Feb 21. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28223350 Free PMC article.
-
Systems Biology and Noninvasive Imaging of Atherosclerosis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Feb;36(2):e1-8. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.306350. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 26819466 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Identification of Critical Paraoxonase 1 Residues Involved in High Density Lipoprotein Interaction.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jan 22;291(4):1890-1904. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.678334. Epub 2015 Nov 13. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26567339 Free PMC article.
-
Human cerebrospinal fluid contains diverse lipoprotein subspecies enriched in proteins implicated in central nervous system health.Sci Adv. 2023 Sep;9(35):eadi5571. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adi5571. Epub 2023 Aug 30. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37647397 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Determinants of Variation in Cholesterol Efflux: Observations from the Dallas Heart Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 24;24(21):15526. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115526. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958510 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alwan A, Global status report on noncommunlcable diseases 2010. World Health Organization: 2011.
-
- Rezaee F; Casetta B; Levels JH; Speijer D; Meijers JC, Proteomic analysis of high-density lipoprotein. Proteomics 2006, 6, (2), 721–30. - PubMed
-
- Vaisar T; Pennathur S; Green PS; Gharib SA; Hoofnagle AN; Cheung MC; Byun J; Vuletic S; Kassim S; Singh P; Chea H; Knopp RH; Brunzell J; Geary R; Chait A; Zhao XQ; Elkon K; Marcovina S; Ridker P; Oram JF; Heinecke JW, Shotgun proteomics implicates protease inhibition and complement activation in the antiinflammatory properties of HDL. J Clin Invest 2007, 117, (3), 746–56. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Karlsson H; Leanderson P; Tagesson C; Lindahl M, Lipoproteomics II: mapping of proteins in high-density lipoprotein using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2005, 5, (5), 1431–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

