Tumour-suppressive microRNA-144-5p directly targets CCNE1/2 as potential prognostic markers in bladder cancer
- PMID: 26057453
- PMCID: PMC4506384
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2015.195
Tumour-suppressive microRNA-144-5p directly targets CCNE1/2 as potential prognostic markers in bladder cancer
Abstract
Background: Analysis of a microRNA (miRNA) expression signature of bladder cancer (BC) by deep-sequencing revealed that clustered miRNAs microRNA (miR)-451a, miR-144-3p, and miR-144-5p were significantly downregulated in BC tissues. We hypothesised that these miRNAs function as tumour suppressors in BC. The aim of this study was to investigate the functional roles of these miRNAs and their modulation of cancer networks in BC cells.
Methods: The functional studies of BC cells were performed using transfection of mature miRNAs. Genome-wide gene expression analysis, in silico analysis, and dual-luciferase reporter assays were applied to identify miRNA targets. The association between miR-144-5p levels and expression of the target genes was determined, and overall patient survival as a function of target gene expression was estimated by the Kaplan-Meier method.
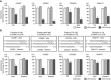
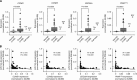
Results: Gain-of-function studies showed that miR-144-5p significantly inhibited cell proliferation by BC cells. Four cell cycle-related genes (CCNE1, CCNE2, CDC25A, and PKMYT1) were identified as direct targets of miR-144-5p. The patients with high CCNE1 or CCNE2 expression had lower overall survival probabilities than those with low expression (P=0.025 and P=0.032).
Conclusion: miR-144-5p functions as tumour suppressor in BC cells. CCNE1 and CCNE2 were directly regulated by miR-144-5p and might be good prognostic markers for survival of BC patients.
Figures



References
-
- Brunetto E, Ferrara AM, Rampoldi F, Talarico A, Cin ED, Grassini G, Spagnuolo L, Sassi I, Ferro A, Cuorvo LV, Barbareschi M, Piccinin S, Maestro R, Pecciarini L, Doglioni C, Cangi MG. CDC25A protein stability represents a previously unrecognized target of HER2 signaling in human breast cancer: implication for a potential clinical relevance in trastuzumab treatment. Neoplasia. 2013;15:579–590. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cai J, Liu X, Cheng J, Li Y, Huang X, Li Y, Ma X, Yu H, Liu H, Wei R. MicroRNA-200 is commonly repressed in conjunctival MALT lymphoma, and targets cyclin E2. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012;250:523–531. - PubMed
-
- Chiyomaru T, Seki N, Inoguchi S, Ishihara T, Mataki H, Matsushita R, Goto Y, Nishikawa R, Tatarano S, Itesako T, Nakagawa M, Enokida H. Dual regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase genes EGFR and c-Met by the tumor-suppressive microRNA-23b/27b cluster in bladder cancer. Int J Oncol. 2015;46:487–496. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

