Fibrinolytic therapy for parapneumonic empyema during pregnancy
- PMID: 26057709
- PMCID: PMC3920424
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rmedc.2011.08.005
Fibrinolytic therapy for parapneumonic empyema during pregnancy
Abstract
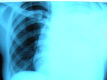
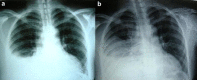
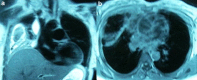
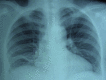
Pneumonia and parapneumonic complicated effusion during pregnancy is uncommon but poses potentially serious risks to both mother and fetus. Enzymatic debridement of the pleural cavity with fibrinolytic agents is a noninvasive option that can facilitate drainage and prevent the need for surgery. Herein, we describe the cases of two pregnant women with parapneumonic empyema who were successfully treated with intrapleural fibrinolytic therapy.
Keywords: Intrapleural fibrinolytic therapy; Parapneumonic empyema; Pregnancy.
Figures


References
-
- Bouros D., Tzouvelekis A., Antoniou K.M., Heffner J.E. Intrapleural fibrinolytic therapy for pleural infection. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2007;20:616–626. - PubMed
-
- Goodnight W.H., Soper D.E. Pneumonia in pregnancy. Crit Care Med. 2005;33(Suppl):390–397. - PubMed
-
- Maskell N.A., Christopher W.H., Davies M.D. Controlled trial of intrapleural streptokinase for pleural infection. N Eng J Med. 2005;352:865–874. - PubMed
-
- Tokuda Y., Matsushima D., Stein G.H., Miyagi S. Intrapleural fibrinolytic agents for empyema and complicated parapneumonic effusions. Chest. 2006;129:783–790. - PubMed
-
- Misthos P., Sepsas E., Konstantinou M., Athanassiadi K., Skottis I., Lioulias A. Early use of intrapleural fibrinolytics in management of postpneumonic empyema. A prospective study. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2005;28:599–603. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

