The Effect of Growth Hormone Administration on the Regulation of Mitochondrial Apoptosis in-Vivo
- PMID: 26057745
- PMCID: PMC4490471
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms160612753
The Effect of Growth Hormone Administration on the Regulation of Mitochondrial Apoptosis in-Vivo
Abstract
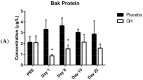
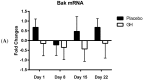
The purpose of this study was to determine whether recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) would show any significant effects on the expression of apoptosis regulating proteins in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Additionally, the potential for post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression by miRNA was assessed in two cellular compartments, the cytosol and the mitochondria. Ten male subjects were subcutaneously injected with either rhGH (1 mg) or saline (0.9%) for seven consecutive days in a double-blinded fashion. Blood sampling was undertaken prior to treatment administration and over a period of three weeks following treatment cessation. Bcl-2 and Bak gene and protein expression levels were measured in PBMCs, while attention was also directed to the expression of miR-181a and miR-125b, known translational inhibitors of Bcl-2 and Bak respectively. Results showed that rhGH significantly decreased Bak protein concentrations compared to placebo samples for up to 8 days post treatment. While cytosolic miRNA expression was not found to be significantly affected by rhGH, measurement of the expression of miR-125b in mitochondrial fractions showed a significant down-regulation eight days post-rhGH administration. These findings suggest that rhGH induces short-term anti-apoptotic effects which may be partially mediated through a novel pathway that alters the concentration of mitochondrially-associated miRNAs.
Keywords: Bcl-2 proteins; growth hormone; mito-miRNAs; mitochondrial apoptosis.
Figures




References
-
- Kandasamy K., Srinivasula S.M., Alnemri E.S., Thompson C.B., Korsmeyer S.J., Bryant J.L., Srivastava R.K. Involvement of proapoptotic molecules Bax and Bak in tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced mitochondrial disruption and apoptosis: Differential regulation of cytochrome c and Smac/DIABLO release. Cancer Res. 2003;63:1712–1721. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

