Structural basis of Keap1 interactions with Nrf2
- PMID: 26057936
- PMCID: PMC4668279
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.05.034
Structural basis of Keap1 interactions with Nrf2
Abstract
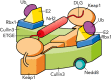
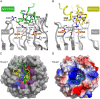
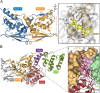
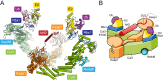
Keap1 is a highly redox-sensitive member of the BTB-Kelch family that assembles with the Cul3 protein to form a Cullin-RING E3 ligase complex for the degradation of Nrf2. Oxidative stress disables Keap1, allowing Nrf2 protein levels to accumulate for the transactivation of critical stress response genes. Consequently, the Keap1-Nrf2 system is extensively pursued for the development of protein-protein interaction inhibitors that will stabilize Nrf2 for therapeutic effect in conditions of neurodegeneration, inflammation, and cancer. Here we review current progress toward the structure determination of Keap1 and its protein complexes with Cul3, Nrf2 substrate, and small-molecule antagonists. Together the available structures establish a rational three-dimensional model to explain the two-site binding of Nrf2 as well as its efficient ubiquitination.
Keywords: BTB; Cullin; Free radicals; Keap1; Kelch; Nrf2; Ubiquitin.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Hayes J.D., Dinkova-Kostova A.T. The Nrf2 regulatory network provides an interface between redox and intermediary metabolism. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014;39:199–218. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki T., Motohashi H., Yamamoto M. Toward clinical application of the Keap1–Nrf2 pathway. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013;34:340–346. - PubMed
-
- Giudice A., Montella M. Activation of the Nrf2–ARE signaling pathway: a promising strategy in cancer prevention. Bioessays. 2006;28:169–181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

