Azotobacter Genomes: The Genome of Azotobacter chroococcum NCIMB 8003 (ATCC 4412)
- PMID: 26061173
- PMCID: PMC4465626
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127997
Azotobacter Genomes: The Genome of Azotobacter chroococcum NCIMB 8003 (ATCC 4412)
Abstract
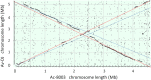
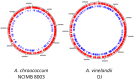
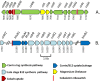
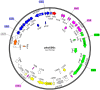
The genome of the soil-dwelling heterotrophic N2-fixing Gram-negative bacterium Azotobacter chroococcum NCIMB 8003 (ATCC 4412) (Ac-8003) has been determined. It consists of 7 circular replicons totalling 5,192,291 bp comprising a circular chromosome of 4,591,803 bp and six plasmids pAcX50a, b, c, d, e, f of 10,435 bp, 13,852, 62,783, 69,713, 132,724, and 311,724 bp respectively. The chromosome has a G+C content of 66.27% and the six plasmids have G+C contents of 58.1, 55.3, 56.7, 59.2, 61.9, and 62.6% respectively. The methylome has also been determined and 5 methylation motifs have been identified. The genome also contains a very high number of transposase/inactivated transposase genes from at least 12 of the 17 recognised insertion sequence families. The Ac-8003 genome has been compared with that of Azotobacter vinelandii ATCC BAA-1303 (Av-DJ), a derivative of strain O, the only other member of the Azotobacteraceae determined so far which has a single chromosome of 5,365,318 bp and no plasmids. The chromosomes show significant stretches of synteny throughout but also reveal a history of many deletion/insertion events. The Ac-8003 genome encodes 4628 predicted protein-encoding genes of which 568 (12.2%) are plasmid borne. 3048 (65%) of these show > 85% identity to the 5050 protein-encoding genes identified in Av-DJ, and of these 99 are plasmid-borne. The core biosynthetic and metabolic pathways and macromolecular architectures and machineries of these organisms appear largely conserved including genes for CO-dehydrogenase, formate dehydrogenase and a soluble NiFe-hydrogenase. The genetic bases for many of the detailed phenotypic differences reported for these organisms have also been identified. Also many other potential phenotypic differences have been uncovered. Properties endowed by the plasmids are described including the presence of an entire aerobic corrin synthesis pathway in pAcX50f and the presence of genes for retro-conjugation in pAcX50c. All these findings are related to the potentially different environmental niches from which these organisms were isolated and to emerging theories about how microbes contribute to their communities.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Beijerinck MW. (1901) Sur des microbes oligonitrophiles. Archives néerl. Science (Series 2) 8: 190–217.
-
- Lipman JG. (1903) Experiments on the transformation and fixation of nitrogen by bacteria. Rep New Jers St Agric Exp Stn 24th (1902/1903). 217–285.
-
- Lipman JG. (1904) Soil bacteriological studies. Further contributions to the physiology and morphology of members of the Azotobacter group. Rep. New Jers. St. Agric. Exp. Stn. 25th: 237–289.
-
- Krasil’nikov NA. (1949) Guide to the bacteria and actinomycetes (R.) Akad Nauk SSSR, Moscow.
-
- Kirakosyan AV, Melkonyan Z S. (1964) New Azotobacter agile varieties from the soils of ARMSSR. Dokl Akad Nauk Armyan 17: 33–42.
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

