Pathogenic Transdifferentiation of Th17 Cells Contribute to Perpetuation of Rheumatoid Arthritis during Anti-TNF Treatment
- PMID: 26062018
- PMCID: PMC4607618
- DOI: 10.2119/molmed.2015.00057
Pathogenic Transdifferentiation of Th17 Cells Contribute to Perpetuation of Rheumatoid Arthritis during Anti-TNF Treatment
Abstract
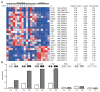
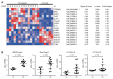
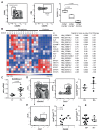
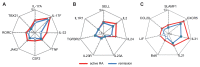
T-helper cells producing interleukin (IL)-17A and IL-17F cytokines (Th17 cells) are considered the source of autoimmunity in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In this study, we characterized specific pathogenic features of Th17 cells in RA. By using nano-string technology, we analyzed transcription of 419 genes in the peripheral blood CCR6(+)CXCR3(-) CD4(+) cells of 14 RA patients and 6 healthy controls and identified 109 genes discriminating Th17 cells of RA patients from the controls. Th17 cells of RA patients had an aggressive pathogenic profile and in addition to signature cytokines IL-17, IL-23 and IL-21, and transcriptional regulators RAR-related orphan receptor gamma of T cells (RORγt) and Janus kinase 2 (JAK2), they produced high levels of IL-23R, C-C chemokine ligand type 20 (CCL20), granulocyte-monocyte colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF ) and transcription factor Tbet required for synovial homing. We showed that Th17 cells are enriched with Helios-producing Foxp3- and IL2RA-deficient cells, indicating altered regulatory profile. The follicular T-helper (Tfh) cells presented a functional profile of adaptor molecules, transcriptional regulator Bcl-6 and B-cell activating cytokines IL-21, IL-31 and leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF ). We observed that anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) treatment had a limited effect on the transcription signature of Th17 cells. Patients in remission retained the machinery of receptors (IL-23R and IL-1R1), proinflammatory cytokines (IL-17F, IL-23, IL-21 and TNF ) and adaptor molecules (C-X-C chemokine receptor 5 [CXCR5] and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 [CTLA-4]), essential for efficient transdifferentiation and accumulation of Th17 cells. This study convincingly shows that the peripheral blood CCR6(+)CXCR3(-) CD4(+) cells of RA patients harbor pathogenic subsets of Th17 and Tfh cells, which may transdifferentiate from Tregs and contribute to perpetuation of the disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aberrant expression of USF2 in refractory rheumatoid arthritis and its regulation of proinflammatory cytokines in Th17 cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Dec 1;117(48):30639-30648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2007935117. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 33203678 Free PMC article.
-
Conventional Tregs in treatment-naïve rheumatoid arthritis are deficient in suppressive function with an increase in percentage of CXCR3 and CCR6 expressing Tregs.Immunol Res. 2024 Jun;72(3):396-408. doi: 10.1007/s12026-023-09444-7. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Immunol Res. 2024. PMID: 38151700
-
The immunomodulatory effects of TNF-α inhibitors on human Th17 cells via RORγt histone acetylation.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 31;8(5):7559-7571. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13791. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27926504 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms underpinning T helper 17 cell heterogeneity and functions in rheumatoid arthritis.J Autoimmun. 2018 Feb;87:69-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2017.12.006. Epub 2017 Dec 16. J Autoimmun. 2018. PMID: 29254845 Review.
-
The role and modulation of CCR6+ Th17 cell populations in rheumatoid arthritis.Cytokine. 2015 Jul;74(1):43-53. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.02.002. Epub 2015 Mar 28. Cytokine. 2015. PMID: 25828206 Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin 22 and its association with neurodegenerative disease activity.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 13;13:958022. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.958022. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36176437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Survivin co-ordinates formation of follicular T-cells acting in synergy with Bcl-6.Oncotarget. 2015 Aug 21;6(24):20043-57. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4994. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26343374 Free PMC article.
-
Levels of Pathogenic Th17 and Th22 Cells in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.J Immunol Res. 2022 Aug 13;2022:5398743. doi: 10.1155/2022/5398743. eCollection 2022. J Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 35996623 Free PMC article.
-
IL-23R Deficiency Does Not Impact Atherosclerotic Plaque Development in Mice.J Am Heart Assoc. 2018 Apr 4;7(8):e008257. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.008257. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018. PMID: 29618473 Free PMC article.
-
IL-21 gene rs6822844 polymorphism and rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility.Biosci Rep. 2020 Jan 31;40(1):BSR20191449. doi: 10.1042/BSR20191449. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31763680 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miossec P, Korn T, Kuchroo VK. Interleukin-17 and type 17 helper T cells. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:888–98. - PubMed
-
- Koenders MI, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-interleukin-17 interplay induces S100A8, interleukin-1beta, and matrix metalloproteinases, and drives irreversible cartilage destruction in murine arthritis: rationale for combination treatment during arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:2329–39. - PubMed
-
- Stamp LK, James MJ, Cleland LG. Interleukin-17: the missing link between T-cell accumulation and effector cell actions in rheumatoid arthritis? Immunol Cell Biol. 2004;82:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Shen H, Goodall JC, Hill Gaston JS. Frequency and phenotype of peripheral blood Th17 cells in ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:1647–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

