Effect of Direct-Current Electric Field on Enzymatic Activity and the Concentration of Laccase
- PMID: 26063937
- PMCID: PMC4456496
- DOI: 10.1007/s12088-015-0523-y
Effect of Direct-Current Electric Field on Enzymatic Activity and the Concentration of Laccase
Abstract
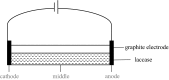
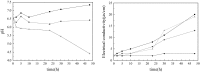
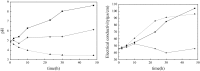
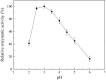
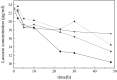
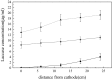
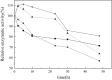
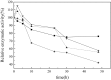
This work investigates the effect of direct-current electric field on the extracellular enzymatic activity, concentration and other experimental parameters of laccase from Trametes versicolor. The results showed that laccase could significantly contribute to the change of pH at the end of graphite electrode. In addition, it increased the electrical conductivity of the water. In the experiment, the optimum pH and catalytic pH range for laccase activity were 3.0 and pH 2.5-4.0. The application of 6 V direct current showed significant effects on the laccase enzyme activity. The activity of laccase was enhanced in the anodic region, but at the same time was strongly inhibited at the cathode. The electric charge characteristics of laccase were changed when exposed to electric field, and some laccases molecules moved to the anode, which produced a slight migration phenomenon. This study is the basis of combination of laccase and electrical technology, at the same time, providing a new direction of enhancing laccase activity. Compared to immobilization, using electric field is simple, no chemical additives, and great potential.
Keywords: Concentration; Direct-current electric field; Enzymatic activity; Laccase.
Figures
References
-
- Reddy KR, Darko-Kagya K, Al-Hamdan AZ. Electrokinetic remediation of pentachlorophenol contaminated clay soil. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011;221:35–44. doi: 10.1007/s11270-011-0767-z. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
