Differential Role of Leptin and Adiponectin in Cardiovascular System
- PMID: 26064110
- PMCID: PMC4433709
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/534320
Differential Role of Leptin and Adiponectin in Cardiovascular System
Abstract
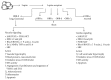
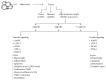
Leptin and adiponectin are differentially expressed adipokines in obesity and cardiovascular diseases. Leptin levels are directly associated with adipose tissue mass, while adiponectin levels are downregulated in obesity. Although significantly produced by adipocytes, leptin is also produced by vascular smooth muscle cells and cardiomyocytes. Plasma leptin concentrations are elevated in cases of cardiovascular diseases, such as hypertension, congestive heart failure, and myocardial infarction. As for the event of left ventricular hypertrophy, researchers have been stirring controversy about the role of leptin in this form of cardiac remodeling. In this review, we discuss how leptin has been shown to play an antihypertrophic role in the development of left ventricular hypertrophy through in vitro experiments, population-based cross-sectional studies, and longitudinal cohort studies. Conversely, we also examine how leptin may actually promote left ventricular hypertrophy using in vitro analysis and human-based univariate and multiple linear stepwise regression analysis. On the other hand, as opposed to leptin's generally detrimental effects on the cardiovascular system, adiponectin is a cardioprotective hormone that reduces left ventricular and vascular hypertrophy, oxidative stress, and inflammation. In this review, we also highlight adiponectin signaling and its protective actions on the cardiovascular system.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiomyocyte Antihypertrophic Effect of Adipose Tissue Conditioned Medium from Rats and Its Abrogation by Obesity is Mediated by the Leptin to Adiponectin Ratio.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 5;11(1):e0145992. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145992. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26731409 Free PMC article.
-
The potential contribution of circulating and locally produced leptin to cardiac hypertrophy and failure.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013 Nov;91(11):883-8. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2013-0057. Epub 2013 May 8. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24117255 Review.
-
Association of serum leptin and adiponectin concentrations with echocardiographic parameters and pathophysiological states in patients with cardiovascular disease receiving cardiovascular surgery.PLoS One. 2019 Nov 8;14(11):e0225008. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225008. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31703113 Free PMC article.
-
Overweight, hypertension and cardiovascular disease: focus on adipocytokines, insulin, weight changes and natriuretic peptides.Dan Med J. 2015 Nov;62(11):B5163. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 26522487
-
[Leptin as a mediator between obesity and cardiac dysfunction].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2012 May 23;66:267-74. doi: 10.5604/17322693.997817. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2012. PMID: 22706112 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Myocardial Extracellular Matrix Dynamic Changes in Myocardial Infarction and Postinfarct Remodeling.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2020;16(1):11-24. doi: 10.2174/1573403X15666190509090832. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2020. PMID: 31072294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurohumoral Integration of Cardiovascular Function by the Lamina Terminalis.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2015 Dec;17(12):93. doi: 10.1007/s11906-015-0602-9. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2015. PMID: 26531751 Review.
-
Analysis of the Associations of Measurements of Body Composition and Inflammatory Factors with Cardiovascular Disease and Its Comorbidities in a Community-Based Study.Biomedicines. 2024 May 11;12(5):1066. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12051066. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38791028 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics reveals an entanglement of fasting leptin concentrations with fatty acid oxidation and gluconeogenesis in healthy children.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 17;12(8):e0183185. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183185. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28817652 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin resistance-related circulating predictive markers in the metabolic syndrome: a systematic review in the Iranian population.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2023 Dec 30;23(1):199-213. doi: 10.1007/s40200-023-01347-6. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2023. PMID: 38932859 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

