Role of Rho kinase signal pathway in inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 26064197
- PMCID: PMC4443031
Role of Rho kinase signal pathway in inflammatory bowel disease
Abstract
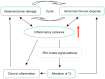
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is nonspecific inflammation in the intestinal track, including Ulcerative Colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD). The incidence of IBD has increased significantly, with its numerous rising up to five million globally, more than 1,700,000 in China. Pathological character of IBD is the inflammation of intestinal mucosa and intestinal fibrosis. Although the pathogenesis of the disease has not yet been fully clarified, some evidence suggests that excessive intestinal inflammation reaction, intestinal barrier impairment and abnormal immune response can initiate IBD. As research continues, some of them have provided new insights toward understanding of Rho kinase signal pathway function at the occurrence and development of IBD. This review aims to summarize the general principles of Rho kinase signal pathway in the pathological procedure of IBD.
Keywords: IBD; Rho/Rho kinase; intestinal barrier; intestinal fibrosis.
Figures



References
-
- Van Aelst L, D’Souza-Schorey C. Rho GTPases and signaling networks. Genes Dev. 1997;11:2295–2322. - PubMed
-
- Boguski MS, McCormick F. Proteins regulating Ras and its relatives. Nature. 1993;366:643–654. - PubMed
-
- Ishizaki T, Uehata M, Tamechika I, Keel J, Nonomura K, Maekawa M, Narumiya S. Pharmacological properties of Y-27632, a specific inhibitor of rho-associated kinases. Mol Pharmacol. 2000;57:976–983. - PubMed
-
- Ikeda S, Satoh K, Kikuchi N, Miyata S, Suzuki K, Omura J, Shimizu T, Kobayashi K, Kobayashi K, Fukumoto Y, Sakata Y, Shimokawa H. Crucial role of rho-kinase in pressure overload-induced right ventricular hypertrophy and dysfunction in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34:1260–1271. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
