Perceptive barriers to peritoneal dialysis implementation: an opinion poll among the French-speaking Belgian nephrologists
- PMID: 26064506
- PMCID: PMC4400486
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sft041
Perceptive barriers to peritoneal dialysis implementation: an opinion poll among the French-speaking Belgian nephrologists
Abstract
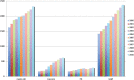
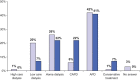
Although peritoneal dialysis (PD) is recognized as an effective renal replacement therapy (RRT) alternative to haemodialysis (HD), its prevalence is around 15% in most of the industrialized countries. In the French-speaking part of Belgium, PD is clearly underused with a prevalence of 8.7% in 2009. The main objectives of this work were to evaluate the nephrologists' perceived obstacles to PD implementation and reflect on possible actions towards PD development. A computer-based 33-item questionnaire was sent by e-mail to all nephrologists affiliated to the French-speaking association. Among 120 adult nephrologists targeted by this inquiry, 97 completed the online questionnaire (response rate 80.8%). Among them, 29% had little experience with PD (treating less than five patients) and 39% reported no specific training with this modality of RRT. However, 88% of responders claimed PD prevalence should be around 20-25%. Half of the responders would choose PD as a first RRT option if they required RRT for themselves. The three main reasons given to the low prevalence of PD were an easy access to HD, patient refusal and lack of nephrologist motivation. Almost all the nephrologists insisted on the need for a dedicated nursing team delivering an effective educational programme and PD management and care. They believe that PD could and should be implemented in Belgium. Enhanced nephrologist motivation and training in PD were identified as predominant factors to be upgraded, as well as patient education programmes.
Keywords: barriers; educational nephrology; peritoneal dialysis; pre-dialysis care; renal replacement therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Lo WK. Peritoneal dialysis utilization and outcome: what are we facing? Perit Dial Int. 2007;27:S42–S47. - PubMed
-
- Van Biesen W, Davies S, Lameire N. An integrated approach to end-stage renal disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2001;16:7–9. doi:10.1093/ndt/16.suppl_6.7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Van Biesen W, Veys N, Lameire N, et al. Why less success of peritoneal dialysis programmes in Europe? Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23:1478–1481. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfn123. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Viglino G, Neri L, Alloati S, et al. Analysis of the factors conditioning the diffusion of peritoneal dialysis in Italy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007;22:3601–3605. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfm416. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bouvier N, Durand PY, Testa A, et al. Regional discrepancies in peritoneal dialysis utilization in France: the role of the nephrologist́s opinion about peritoneal dialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24:1293–1297. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfn648. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

