Diabetic Kidney Disease: Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Targets
- PMID: 26064987
- PMCID: PMC4430644
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/697010
Diabetic Kidney Disease: Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Targets
Abstract
Diabetes is a worldwide epidemic that has led to a rise in diabetic kidney disease (DKD). Over the past two decades, there has been significant clarification of the various pathways implicated in the pathogenesis of DKD. Nonetheless, very little has changed in the way clinicians manage patients with this disorder. Indeed, treatment is primarily centered on controlling hyperglycemia and hypertension and inhibiting the renin-angiotensin system. The purpose of this review is to describe the current understanding of how the hemodynamic, metabolic, inflammatory, and alternative pathways are all entangled in pathogenesis of DKD and detail the various therapeutic targets that may one day play a role in quelling this epidemic.
Figures
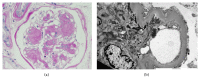


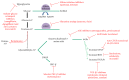
References
-
- Number (in Millions) of Civilian, Noninstitutionalized Adults with Diagnosed Diabetes, United States, 1980–2011, http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/statistics/prev/national/figadults.htm.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Annual Number (in Thousands) of New Cases of Diagnosed Diabetes Among Adults Aged 18–79 Years, United States, 1980–2011. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2012. http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/statistics/incidence/fig1.htm.
-
- USRDS: the United States renal data system. American Journal of Kidney Diseases. 2003;42(6, supplement 5):1–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

