Contour-Driven Atlas-Based Segmentation
- PMID: 26068202
- PMCID: PMC4756595
- DOI: 10.1109/TMI.2015.2442753
Contour-Driven Atlas-Based Segmentation
Abstract
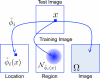
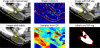
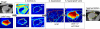
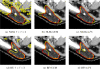
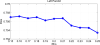
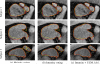
We propose new methods for automatic segmentation of images based on an atlas of manually labeled scans and contours in the image. First, we introduce a Bayesian framework for creating initial label maps from manually annotated training images. Within this framework, we model various registration- and patch-based segmentation techniques by changing the deformation field prior. Second, we perform contour-driven regression on the created label maps to refine the segmentation. Image contours and image parcellations give rise to non-stationary kernel functions that model the relationship between image locations. Setting the kernel to the covariance function in a Gaussian process establishes a distribution over label maps supported by image structures. Maximum a posteriori estimation of the distribution over label maps conditioned on the outcome of the atlas-based segmentation yields the refined segmentation. We evaluate the segmentation in two clinical applications: the segmentation of parotid glands in head and neck CT scans and the segmentation of the left atrium in cardiac MR angiography images.
Figures

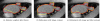


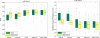
References
-
- Ashburner J, Friston K. Unified segmentation. Neuroimage. 2005;26(3):839–851. - PubMed
-
- Pohl K, Fisher J, Grimson W, Kikinis R, Wells W. A Bayesian model for joint segmentation and registration. Neuroimage. 2006;31(1):228–239. - PubMed
-
- D'Agostino E, Maes F, Vandermeulen D, Suetens P. A unified framework for atlas based brain image segmentation and registration. WBIR. 2006
-
- Heckemann R, Hajnal J, Aljabar P, Rueckert D, Hammers A. Automatic anatomical brain MRI segmentation combining label propagation and decision fusion. NeuroImage. 2006;33(1):115–126. - PubMed
-
- Rohlfing T, Brandt R, Menzel R, Maurer C, et al. Evaluation of atlas selection strategies for atlas-based image segmentation with application to confocal microscopy images of bee brains. NeuroImage. 2004;21(4):1428–1442. - PubMed

