Small-molecule activation of SERCA2a SUMOylation for the treatment of heart failure
- PMID: 26068603
- PMCID: PMC4467461
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8229
Small-molecule activation of SERCA2a SUMOylation for the treatment of heart failure
Abstract
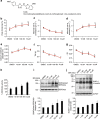
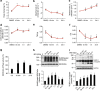
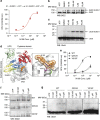
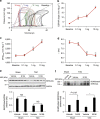
Decreased activity and expression of the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase (SERCA2a), a critical pump regulating calcium cycling in cardiomyocyte, are hallmarks of heart failure. We have previously described a role for the small ubiquitin-like modifier type 1 (SUMO-1) as a regulator of SERCA2a and have shown that gene transfer of SUMO-1 in rodents and large animal models of heart failure restores cardiac function. Here, we identify and characterize a small molecule, N106, which increases SUMOylation of SERCA2a. This compound directly activates the SUMO-activating enzyme, E1 ligase, and triggers intrinsic SUMOylation of SERCA2a. We identify a pocket on SUMO E1 likely to be responsible for N106's effect. N106 treatment increases contractile properties of cultured rat cardiomyocytes and significantly improves ventricular function in mice with heart failure. This first-in-class small-molecule activator targeting SERCA2a SUMOylation may serve as a potential therapeutic strategy for treatment of heart failure.
Conflict of interest statement
R.J.H. is the scientific cofounder of Celladon Corporation, which is developing AAV1.SERCA2a for the treatment of HF. All other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Zsebo K. et al.. Long-term effects of AAV1/SERCA2a gene transfer in patients with severe heart failure: analysis of recurrent cardiovascular events and mortality. Circ. Res. 114, 101–108 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

