Gender difference in adiponectin associated with cardiovascular mortality
- PMID: 26068642
- PMCID: PMC4631110
- DOI: 10.1186/s12881-015-0187-9
Gender difference in adiponectin associated with cardiovascular mortality
Abstract
Background: It is important to identify cardiovascular diseases in patients at high risk. To include genetics into routine cardiological patients has therefore been discussed recently. We wanted to evaluate the association between high-molecular weight adiponectin and cardiovascular risk, and secondly in the same population evaluate if specific genotype differences regarding risk could be observed, and thirdly if gender differences could be seen.
Method: Four hundred seventy-six elderly participants recruited from a rural community were included. All participants underwent a clinical examination, echocardiography, and blood sampling and the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) (rs266729) of adiponectin was analysed. Follow-up time was 6.7 years.
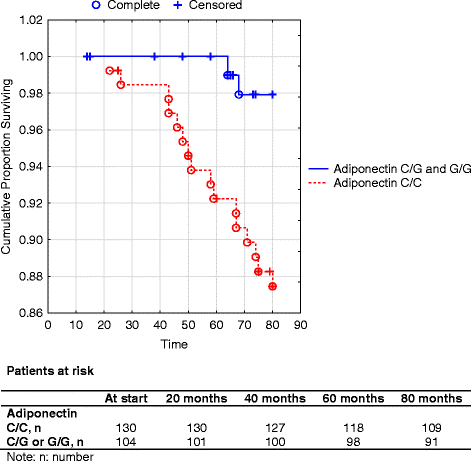
Results: Those with high serum concentration of adiponectin had a more 2 fold increased cardiovascular risk, and it might be that females exhibits even higher risk where a more than 5 fold increased risk could be seen. The result could be demonstrated even in a multivariate model adjusting for well-known clinical risk factors. However, as the sample size was small the gender differences should be interpreted with caution. In the genotype evaluation the C/C carriers of the female group had a more than 9-fold increased risk of cardiovascular mortality, however the confidence interval was wide. Such genotype difference could not be found in the male group.
Conclusion: High level of adiponectin was associated with increased cardiovascular risk. Also a gender difference in the genotype evaluation could be seen where the C/C carriers obtained higher risk in the female group but not in the male group. Thus, in order to identify patients at risk early, genetic analyses may add to the armamentarium used in the clinical routine. However, information should be regarded as hypothesis generating as the sample size was small and should stimulate further research in individualized cardiovascular prevention and treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Waki H, Terauchi Y, Kubota N, Hara K, Mori Y, Ide T, Murakami K, Tsuboyama-Kasaoka N, Ezaki O, Akanuma Y, Gavrilova O, Vinson C, Reitman ML, Kagechika H, Shudo K, Yoda M, Nakano Y, Tobe K, Nagai R, Kimura S, Tomita M, Froguel P, Kadowaki T. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat Med. 2001;7:941–6. doi: 10.1038/90984. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arita Y, Kihara S, Ouchi N, Takahashi M, Maeda K, Miyagawa J, Hotta K, Shimomura I, Nakamura T, Miyaoka K, Kuriyama H, Nishida M, Yamashita S, Okubo K, Matsubara K, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y. Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;257:79–83. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.0255. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

