Brief Report: Gonorrhea and Chlamydia Testing Increasing but Still Lagging in HIV Clinics in the United States
- PMID: 26068721
- PMCID: PMC4607588
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000000711
Brief Report: Gonorrhea and Chlamydia Testing Increasing but Still Lagging in HIV Clinics in the United States
Abstract
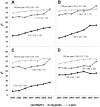
Screening persons living with HIV for gonorrhea and chlamydia has been recommended since 2003. We compared annual gonorrhea/chlamydia testing to syphilis and lipid testing among 19,368 adults (41% men who have sex with men, 30% heterosexual men, and 29% women) engaged in HIV care. In 2004, 22%, 62%, and 70% of all patients were tested for gonorrhea/chlamydia, syphilis, and lipid levels, respectively. Despite increasing steadily [odds ratio per year (95% confidence interval): 1.14 (1.13 to 1.15)], gonorrhea/chlamydia testing in 2010 remained lower than syphilis and lipid testing (39%, 77%, 76%, respectively). Interventions to improve gonorrhea/chlamydia screening are needed. A more targeted screening approach may be warranted.
Figures
References
-
- Soni S, White JA. Self-screening for neisseria gonorrhoeae and chlamydia trachomatis in the Human Immunodeficiency Virus clinic--high yields and high acceptability. Sex Transm Dis. 2011;38(12):1107–1109. - PubMed
-
- Phipps W, Stanley H, Kohn R, Stansell J, Klausner JD. Syphilis, chlamydia, and gonorrhea screening in HIV-infected patients in primary care, San Francisco, California, 2003. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2005;19(8):495–8. - PubMed
-
- Farley TA, Cohen DA, Wu SY, Besch CL. The value of screening for sexually transmitted diseases in an HIV clinic. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2003;33(5):642–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical