Mini-Open Anterior Retroperitoneal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion for Lumbar Spinal Degeneration Disease
- PMID: 26069130
- PMCID: PMC4479835
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.4.1051
Mini-Open Anterior Retroperitoneal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion for Lumbar Spinal Degeneration Disease
Abstract
Purpose: Surgery for lumbar spinal degeneration disease is widely performed. While posterior decompression and fusion are popular, anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) is also used for treatment. Extreme lateral interbody fusion (XLIF) is commonly used for noninvasive ALIF; however, several complications, such as spinal nerve and psoas muscle injury, have been reported. In the current study, we examined the clinical efficacy and complications of oblique lateral interbody fusion (OLIF) for lumbar spinal degeneration disease.
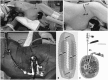
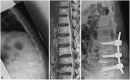
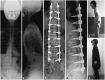
Materials and methods: Thirty-five patients with degenerated spondylolisthesis, discogenic pain, and kyphoscoliosis were examined. All patients underwent OLIF surgery (using a cage and bone graft from the iliac crest) with or without posterior decompression, without real-time electromyography monitoring. Posterior screws were used in all patients. Visual analog scale (VAS) score and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) were evaluated before and 6 months after surgery. Surgical complications were also evaluated.
Results: Pain scores significantly improved after surgery, compared to those before surgery (p<0.05). There was no patient who underwent revision surgery. There was no spinal nerve, major vessel, peritoneal, or urinary injury. Few patients showed symptoms from psoas invasion.
Conclusion: OLIF surgery produced good surgical results without any major complication.
Keywords: Oblique lateral interbody fusion; decompress; degeneration disease; injury; lumbar; nerve; surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Chastain CA, Eck JC, Hodges SD, Humphreys SC, Levi P. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a retrospective study of long-term pain relief and fusion outcomes. Orthopedics. 2007;30:389–392. - PubMed
-
- Gill K, Blumenthal SL. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion. A 2-year follow-up of 238 patients. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 1993;251:108–110. - PubMed
-
- Ishihara H, Osada R, Kanamori M, Kawaguchi Y, Ohmori K, Kimura T, et al. Minimum 10-year follow-up study of anterior lumbar interbody fusion for isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord. 2001;14:91–99. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, Kitahara H, Yamagata M, Murakami M, Takata K, Miyamoto K, et al. Long-term results of anterior interbody fusion for treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1990;15:1211–1215. - PubMed
-
- Tiusanen H, Seitsalo S, Osterman K, Soini J. Retrograde ejaculation after anterior interbody lumbar fusion. Eur Spine J. 1995;4:339–342. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

