Magnesium basics
- PMID: 26069819
- PMCID: PMC4455825
- DOI: 10.1093/ndtplus/sfr163
Magnesium basics
Abstract
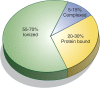
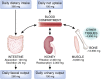
As a cofactor in numerous enzymatic reactions, magnesium fulfils various intracellular physiological functions. Thus, imbalance in magnesium status-primarily hypomagnesaemia as it is seen more often than hypermagnesaemia-might result in unwanted neuromuscular, cardiac or nervous disorders. Measuring total serum magnesium is a feasible and affordable way to monitor changes in magnesium status, although it does not necessarily reflect total body magnesium content. The following review focuses on the natural occurrence of magnesium and its physiological function. The absorption and excretion of magnesium as well as hypo- and hypermagnesaemia will be addressed.
Keywords: hypermagnesaemia; hypomagnesaemia; magnesium; physicochemical properties; physiological function; regulation.
Figures


References
-
- Cotton FA, Wilkinson G. Weilheim, Germany: Chemie GmbH; 1967. Anorganische Chemie.
-
- Weast RC. Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 1987.
-
- Hollemann AF, Wiberg E. Lehrbuch der anorganischen Chemie. Berlin, Germany: De Gruyter; 1964.
-
- Bodaker I, Sharon I, Suzuki MT, et al. Comparative community genomics in the Dead Sea: an increasingly extreme environment. ISME J. 2010;4:399–407. - PubMed
-
- Maguire ME, Cowan JA. Magnesium chemistry and biochemistry. Biometals. 2002;15:203–210. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

