Delivery of Polymeric Nanoparticles to Target Vascular Diseases
- PMID: 26069867
- PMCID: PMC4460796
- DOI: 10.4172/2167-7956.s1-001
Delivery of Polymeric Nanoparticles to Target Vascular Diseases
Abstract
Current advances in nanotechnology have paved the way for the early detection, prevention and treatment of various diseases such as vascular disorders and cancer. These advances have provided novel approaches or modalities of incorporating or adsorbing therapeutic, biosensor and targeting agents into/on nanoparticles. With significant progress, nanomedicine for vascular therapy has shown significant advantages over traditional medicine because of its ability to selectively target the disease site and reduce adverse side effects. Targeted delivery of nanoparticles to vascular endothelial cells or the vascular wall provides an effective and more efficient way for early detection and/or treatment of vascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis and Cerebrovascular Amyloid Angiopathy (CAA). Clinical applications of biocompatible and biodegradable polymers in areas such as vascular graft, implantable drug delivery, stent devices and tissue engineering scaffolds have advanced the candidature of polymers as potential nano-carriers for vascular-targeted delivery of diagnostic agents and drugs. This review focuses on the basic aspects of the vasculature and its associated diseases and relates them to polymeric nanoparticle-based strategies for targeting therapeutic agents to diseased vascular site.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Nanomedicine; Polymeric nanoparticles; Targeted delivery; Thrombosis; Vascular disease.
Figures
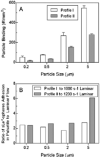

Similar articles
-
Advanced targeted therapies in cancer: Drug nanocarriers, the future of chemotherapy.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015 Jun;93:52-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.03.018. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015. PMID: 25813885 Review.
-
Atherosclerosis and Nanomedicine Potential: Current Advances and Future Opportunities.Curr Med Chem. 2020;27(21):3534-3554. doi: 10.2174/0929867326666190301143952. Curr Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 30827225
-
Biodegradable Polymeric Nanoparticles as the Delivery Carrier for Drug.Curr Drug Deliv. 2016;13(4):494-9. doi: 10.2174/156720181304160521004609. Curr Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 27230997 Review.
-
Natural biodegradable polymers based nano-formulations for drug delivery: A review.Int J Pharm. 2019 Apr 20;561:244-264. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.03.011. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Int J Pharm. 2019. PMID: 30851391 Review.
-
Advances of nanomedicine in treatment of atherosclerosis and thrombosis.Environ Res. 2023 Dec 1;238(Pt 2):116637. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.116637. Epub 2023 Jul 22. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 37482129 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent strategies to design vascular theranostic nanoparticles.Nanotheranostics. 2017 Apr 6;1(2):166-177. doi: 10.7150/ntno.18531. eCollection 2017. Nanotheranostics. 2017. PMID: 29071185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Production of Fluorescent Dissolved Organic Matter by Microalgae Strains from the Ob and Yenisei Gulfs (Siberia).Plants (Basel). 2022 Dec 3;11(23):3361. doi: 10.3390/plants11233361. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36501400 Free PMC article.
-
Systemically administered collagen-targeted gold nanoparticles bind to arterial injury following vascular interventions.Physiol Rep. 2017 Feb;5(4):e13128. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13128. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Physiol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28242820 Free PMC article.
-
Detection and treatment of atherosclerosis using nanoparticles.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2017 Jan;9(1):10.1002/wnan.1412. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1412. Epub 2016 May 31. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2017. PMID: 27241794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in the application of patch materials in cardiovascular surgery.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Feb 28;48(2):285-293. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2023.220560. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 36999476 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
References
-
- Charoenphol P, Mocherla S, Bouis D, Namdee K, Pinsky DJ, et al. Targeting therapeutics to the vascular wall in atherosclerosis--carrier size matters. Atherosclerosis. 2011;217:364–370. - PubMed
-
- Decuzzi P, Lee S, Bhushan B, Ferrari M. A theoretical model for the margination of particles within blood vessels. Ann Biomed Eng. 2005;33:179–190. - PubMed
-
- Ku DN, Giddens DP, Zarins CK, Glagov S. Pulsatile flow and atherosclerosis in the human carotid bifurcation. Positive correlation between plaque location and low oscillating shear stress. Arteriosclerosis. 1985;5:293–302. - PubMed
-
- Gupta AS. Nanomedicine approaches in vascular disease: a review. Nanomedicine. 2011;7:763–779. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
