Discrete BDNF Neurons in the Paraventricular Hypothalamus Control Feeding and Energy Expenditure
- PMID: 26073495
- PMCID: PMC4497865
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.05.008
Discrete BDNF Neurons in the Paraventricular Hypothalamus Control Feeding and Energy Expenditure
Abstract
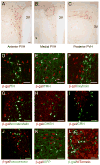
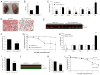
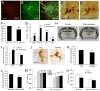
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a key regulator of energy balance; however, its underlying mechanism remains unknown. By analyzing BDNF-expressing neurons in paraventricular hypothalamus (PVH), we have uncovered neural circuits that control energy balance. The Bdnf gene in the PVH was mostly expressed in previously undefined neurons, and its deletion caused hyperphagia, reduced locomotor activity, impaired thermogenesis, and severe obesity. Hyperphagia and reduced locomotor activity were associated with Bdnf deletion in anterior PVH, whereas BDNF neurons in medial and posterior PVH drive thermogenesis by projecting to spinal cord and forming polysynaptic connections to brown adipose tissues. Furthermore, BDNF expression in the PVH was increased in response to cold exposure, and its ablation caused atrophy of sympathetic preganglionic neurons. Thus, BDNF neurons in anterior PVH control energy intake and locomotor activity, whereas those in medial and posterior PVH promote thermogenesis by releasing BDNF into spinal cord to boost sympathetic outflow.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Bachman ES, Dhillon H, Zhang CY, Cinti S, Bianco AC, Kobilka BK, Lowell BB. betaAR signaling required for diet-induced thermogenesis and obesity resistance. Science. 2002;297:843–845. - PubMed
-
- Balthasar N, Dalgaard LT, Lee CE, Yu J, Funahashi H, Williams T, Ferreira M, Tang V, McGovern RA, Kenny CD, et al. Divergence of melanocortin pathways in the control of food intake and energy expenditure. Cell. 2005;123:493–505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

