Mitochondrial cytochrome c biogenesis: no longer an enigma
- PMID: 26073510
- PMCID: PMC4509832
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.05.006
Mitochondrial cytochrome c biogenesis: no longer an enigma
Abstract
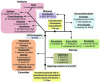
Cytochromes c (cyt c) and c1 are heme proteins that are essential for aerobic respiration. Release of cyt c from mitochondria is an important signal in apoptosis initiation. Biogenesis of c-type cytochromes involves covalent attachment of heme to two cysteines (at a conserved CXXCH sequence) in the apocytochrome. Heme attachment is catalyzed in most mitochondria by holocytochrome c synthase (HCCS), which is also necessary for the import of apocytochrome c (apocyt c). Thus, HCCS affects cellular levels of cyt c, impacting mitochondrial physiology and cell death. Here, we review the mechanisms of HCCS function and the roles of heme and residues in the CXXCH motif. Additionally, we consider concepts emerging within the two prokaryotic cytochrome c biogenesis pathways.
Keywords: cytochrome c; heme attachment; holocytochrome c synthase; mitochondria.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

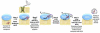


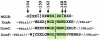
References
-
- Dickerson RE, et al. Ferricytochrome c. I. General features of the horse and bonito proteins at 2.8 A resolution. J. Biol. Chem. 1971;246:1511–1535. - PubMed
-
- Bushnell GW, et al. High-resolution three-dimensional structure of horse heart cytochrome c. J. Mol. Biol. 1990;214:585–595. - PubMed
-
- Iwata S, et al. Complete structure of the 11-subunit bovine mitochondrial cytochrome bc1 complex. Science. 1998;281:64–71. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Z, et al. Electron transfer by domain movement in cytochrome bc1. Nature. 1998;392:677–684. - PubMed
-
- Allen JW, et al. Complexity and diversity in c-type cytochrome biogenesis systems. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005;33:145–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

