Myogenic-specific ablation of Fgfr1 impairs FGF2-mediated proliferation of satellite cells at the myofiber niche but does not abolish the capacity for muscle regeneration
- PMID: 26074812
- PMCID: PMC4446549
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2015.00085
Myogenic-specific ablation of Fgfr1 impairs FGF2-mediated proliferation of satellite cells at the myofiber niche but does not abolish the capacity for muscle regeneration
Abstract
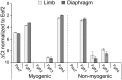
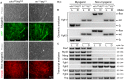
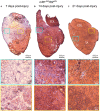
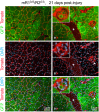
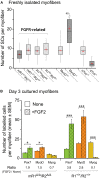
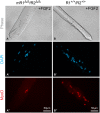
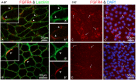
Skeletal muscle satellite cells (SCs) are Pax7(+) myogenic stem cells that reside between the basal lamina and the plasmalemma of the myofiber. In mature muscles, SCs are typically quiescent, but can be activated in response to muscle injury. Depending on the magnitude of tissue trauma, SCs may divide minimally to repair subtle damage within individual myofibers or produce a larger progeny pool that forms new myofibers in cases of overt muscle injury. SC transition through proliferation, differentiation and renewal is governed by the molecular blueprint of the cells as well as by the extracellular milieu at the SC niche. In particular, the role of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family in regulating SCs during growth and aging is well recognized. Of the several FGFs shown to affect SCs, FGF1, FGF2, and FGF6 proteins have been documented in adult skeletal muscle. These prototypic paracrine FGFs transmit their mitogenic effect through the FGFRs, which are transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptors. Using the mouse model, we show here that of the four Fgfr genes, only Fgfr1 and Fgfr4 are expressed at relatively high levels in quiescent SCs and their proliferating progeny. To further investigate the role of FGFR1 in adult myogenesis, we have employed a genetic (Cre/loxP) approach for myogenic-specific (MyoD(Cre)-driven) ablation of Fgfr1. Neither muscle histology nor muscle regeneration following cardiotoxin-induced injury were overtly affected in Fgfr1-ablated mice. This suggests that FGFR1 is not obligatory for SC performance in this acute muscle trauma model, where compensatory growth factor/cytokine regulatory cascades may exist. However, the SC mitogenic response to FGF2 is drastically repressed in isolated myofibers prepared from Fgfr1-ablated mice. Collectively, our study indicates that FGFR1 is important for FGF-mediated proliferation of SCs and its mitogenic role is not compensated by FGFR4 that is also highly expressed in SCs.
Keywords: MyoDCre; Pax7; alpha7 integrin; cardiotoxin injury; fibro/adipogenic progenitors; fibroblast growth factor; muscle spindles; satellite cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gene expression patterns of the fibroblast growth factors and their receptors during myogenesis of rat satellite cells.J Histochem Cytochem. 2000 Aug;48(8):1079-96. doi: 10.1177/002215540004800805. J Histochem Cytochem. 2000. PMID: 10898801
-
Satellite cell-specific ablation of Cdon impairs integrin activation, FGF signalling, and muscle regeneration.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020 Aug;11(4):1089-1103. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12563. Epub 2020 Feb 27. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020. PMID: 32103583 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the transcriptional signature of skeletal muscle stem cells.J Anim Sci. 2008 Apr;86(14 Suppl):E207-16. doi: 10.2527/jas.2007-0473. Epub 2007 Sep 18. J Anim Sci. 2008. PMID: 17878281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation in response to members of the fibroblast growth factor family and hepatocyte growth factor.J Cell Physiol. 1999 Dec;181(3):499-506. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199912)181:3<499::AID-JCP14>3.0.CO;2-1. J Cell Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10528236
-
Muscle Satellite Cell Heterogeneity: Does Embryonic Origin Matter?Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 15;9:750534. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.750534. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34722534 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Skeletal muscle stem cells in comfort and stress.NPJ Regen Med. 2018 Dec 21;3:24. doi: 10.1038/s41536-018-0062-3. eCollection 2018. NPJ Regen Med. 2018. PMID: 30588332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA helicase, DDX27 regulates skeletal muscle growth and regeneration by modulation of translational processes.PLoS Genet. 2018 Mar 8;14(3):e1007226. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007226. eCollection 2018 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 29518074 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profile and overexpression outcome indicate a role for βKlotho in skeletal muscle fibro/adipogenesis.FEBS J. 2016 May;283(9):1653-68. doi: 10.1111/febs.13682. Epub 2016 Apr 13. FEBS J. 2016. PMID: 26881702 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor 6 regulates sizing of the muscle stem cell pool.Stem Cell Reports. 2021 Dec 14;16(12):2913-2927. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2021.10.006. Epub 2021 Nov 4. Stem Cell Reports. 2021. PMID: 34739848 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletal Muscle Regeneration in Cardiotoxin-Induced Muscle Injury Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 2;23(21):13380. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113380. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362166 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

