Scaling Up Family Planning to Reduce Maternal and Child Mortality: The Potential Costs and Benefits of Modern Contraceptive Use in South Africa
- PMID: 26076482
- PMCID: PMC4468244
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130077
Scaling Up Family Planning to Reduce Maternal and Child Mortality: The Potential Costs and Benefits of Modern Contraceptive Use in South Africa
Abstract
Introduction: Family planning contributes significantly to the prevention of maternal and child mortality. However, many women still do not use modern contraception and the numbers of unintended pregnancies, abortions and subsequent deaths are high. In this paper, we estimate the service delivery costs of scaling up modern contraception, and the potential impact on maternal, newborn and child survival in South Africa.
Methods: The Family Planning model in Spectrum was used to project the impact of modern contraception on pregnancies, abortions and births in South Africa (2015-2030). The contraceptive prevalence rate (CPR) was increased annually by 0.68 percentage points. The Lives Saved Tool was used to estimate maternal and child deaths, with coverage of essential maternal and child health interventions increasing by 5% annually. A scenario analysis was done to test impacts when: the change in CPR was 0.1% annually; and intervention coverage increased linearly to 99% in 2030.
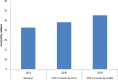
Results: If CPR increased by 0.68% annually, the number of pregnancies would reduce from 1.3 million in 2014 to one million in 2030. Unintended pregnancies, abortions and births decrease by approximately 20%. Family planning can avert approximately 7,000 newborn and child and 600 maternal deaths. The total annual costs of providing modern contraception in 2030 are estimated to be US$33 million and the cost per user of modern contraception is US$7 per year. The incremental cost per life year gained is US$40 for children and US$1,000 for mothers.
Conclusion: Maternal and child mortality remain high in South Africa, and scaling up family planning together with optimal maternal, newborn and child care is crucial. A huge impact can be made on maternal and child mortality, with a minimal investment per user of modern contraception.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Trends in Maternal Mortality: 1990 to 2010. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO, 2012.
-
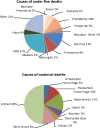
- Stats SA. Mortality and causes of death in South Africa, 2011: Findings from death notification. Pretoria, South Africa: Stats SA, 2014.
-
- Dorrington RE, Bradshaw D, Laubscher R. Rapid mortality surveillance report 2012. Cape Town, South Africa: South African Medical Research Council, 2014.
-
- Stats SA. Millennium Development Goals Country Report. Pretoria, South Africa: Stats SA, 2013.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical