Stress Effects on Neuronal Structure: Hippocampus, Amygdala, and Prefrontal Cortex
- PMID: 26076834
- PMCID: PMC4677120
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2015.171
Stress Effects on Neuronal Structure: Hippocampus, Amygdala, and Prefrontal Cortex
Abstract
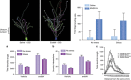
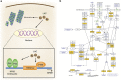
The hippocampus provided the gateway into much of what we have learned about stress and brain structural and functional plasticity, and this initial focus has expanded to other interconnected brain regions, such as the amygdala and prefrontal cortex. Starting with the discovery of adrenal steroid, and later, estrogen receptors in the hippocampal formation, and subsequent discovery of dendritic and spine synapse remodeling and neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus, mechanistic studies have revealed both genomic and rapid non-genomic actions of circulating steroid hormones in the brain. Many of these actions occur epigenetically and result in ever-changing patterns of gene expression, in which there are important sex differences that need further exploration. Moreover, glucocorticoid and estrogen actions occur synergistically with an increasing number of cellular mediators that help determine the qualitative nature of the response. The hippocampus has also been a gateway to understanding lasting epigenetic effects of early-life experiences. These findings in animal models have resulted in translation to the human brain and have helped change thinking about the nature of brain malfunction in psychiatric disorders and during aging, as well as the mechanisms of the effects of early-life adversity on the brain and the body.
Figures







Comment in
-
An Overly Permissive Extension.Perspect Psychol Sci. 2016 Jul;11(4):442-50. doi: 10.1177/1745691616635593. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27474132
References
-
- Ahima R, Krozowski Z, Harlan R (1991). Type I corticosteroid receptor-like immunoreactivity in the rat CNS: distribution and regulation by corticosteroids. J Comp Neurol 313: 522–538. - PubMed
-
- Ahima RS, Harlan RE (1990). Charting of type II glucocorticoid receptor-like immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 39: 579–604. - PubMed
-
- Allfrey VG (1970). Changes in chromosomal proteins at times of gene activation. Fed Proc 29: 1447–1460. - PubMed
-
- Altman J, Das GD (1965). Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J Comp Neurol 124: 319–336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

