CD24 tracks divergent pluripotent states in mouse and human cells
- PMID: 26076835
- PMCID: PMC4490408
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8329
CD24 tracks divergent pluripotent states in mouse and human cells
Abstract
Reprogramming is a dynamic process that can result in multiple pluripotent cell types emerging from divergent paths. Cell surface protein expression is a particularly desirable tool to categorize reprogramming and pluripotency as it enables robust quantification and enrichment of live cells. Here we use cell surface proteomics to interrogate mouse cell reprogramming dynamics and discover CD24 as a marker that tracks the emergence of reprogramming-responsive cells, while enabling the analysis and enrichment of transgene-dependent (F-class) and -independent (traditional) induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) at later stages. Furthermore, CD24 can be used to delineate epiblast stem cells (EpiSCs) from embryonic stem cells (ESCs) in mouse pluripotent culture. Importantly, regulated CD24 expression is conserved in human pluripotent stem cells (PSCs), tracking the conversion of human ESCs to more naive-like PSC states. Thus, CD24 is a conserved marker for tracking divergent states in both reprogramming and standard pluripotent culture.
Figures
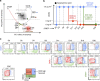
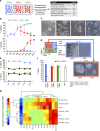
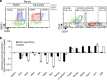
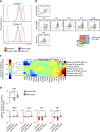
References
-
- Takahashi K. & Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126, 663–676 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Park I.-H. et al. Reprogramming of human somatic cells to pluripotency with defined factors. Nature 451, 141–146 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Samavarchi-Tehrani P. et al. Functional genomics reveals a BMP-driven mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition in the initiation of somatic cell reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell 7, 64–77 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

