Optimal acquisition and modeling parameters for accurate assessment of low Ktrans blood-brain barrier permeability using dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI
- PMID: 26077645
- PMCID: PMC4726482
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.25793
Optimal acquisition and modeling parameters for accurate assessment of low Ktrans blood-brain barrier permeability using dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI
Abstract
Purpose: To determine optimal parameters for acquisition and processing of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI) to detect small changes in near normal low blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability.
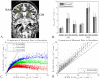
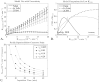
Methods: Using a contrast-to-noise ratio metric (K-CNR) for Ktrans precision and accuracy, the effects of kinetic model selection, scan duration, temporal resolution, signal drift, and length of baseline on the estimation of low permeability values was evaluated with simulations.
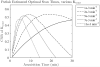
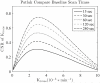
Results: The Patlak model was shown to give the highest K-CNR at low Ktrans . The Ktrans transition point, above which other models yielded superior results, was highly dependent on scan duration and tissue extravascular extracellular volume fraction (ve ). The highest K-CNR for low Ktrans was obtained when Patlak model analysis was combined with long scan times (10-30 min), modest temporal resolution (<60 s/image), and long baseline scans (1-4 min). Signal drift as low as 3% was shown to affect the accuracy of Ktrans estimation with Patlak analysis.
Conclusion: DCE acquisition and modeling parameters are interdependent and should be optimized together for the tissue being imaged. Appropriately optimized protocols can detect even the subtlest changes in BBB integrity and may be used to probe the earliest changes in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and multiple sclerosis.
Keywords: DCE-MRI; Ktrans estimation; blood-brain barrier; parameter optimization; permeability.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Parker GJ, Padhani AR. T1-W DCE-MRI: T1-Weighted Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI. Quantitative MRI of the Brain: Measuring Changes Caused by Disease. 2004:341–364.
-
- Hylton N. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging as an imaging biomarker. Journal of clinical oncology. 2006;24(20):3293–3298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

