Suppression of cell division-associated genes by Helicobacter pylori attenuates proliferation of RAW264.7 monocytic macrophage cells
- PMID: 26078204
- PMCID: PMC4468580
- DOI: 10.1038/srep11046
Suppression of cell division-associated genes by Helicobacter pylori attenuates proliferation of RAW264.7 monocytic macrophage cells
Abstract
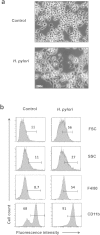
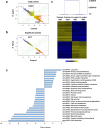
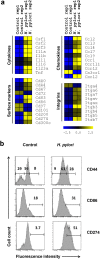
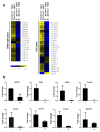
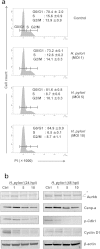
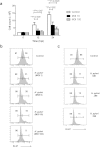
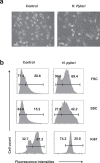
Helicobacter pylori at multiplicity of infection (MOI ≥ 50) have been shown to cause apoptosis in RAW264.7 monocytic macrophage cells. Because chronic gastric infection by H. pylori results in the persistence of macrophages in the host's gut, it is likely that H. pylori is present at low to moderate, rather than high numbers in the infected host. At present, the effect of low-MOI H. pylori infection on macrophage has not been fully elucidated. In this study, we investigated the genome-wide transcriptional regulation of H. pylori-infected RAW264.7 cells at MOI 1, 5 and 10 in the absence of cellular apoptosis. Microarray data revealed up- and down-regulation of 1341 and 1591 genes, respectively. The expression of genes encoding for DNA replication and cell cycle-associated molecules, including Aurora-B kinase (AurkB) were down-regulated. Immunoblot analysis verified the decreased expression of AurkB and downstream phosphorylation of Cdk1 caused by H. pylori infection. Consistently, we observed that H. pylori infection inhibited cell proliferation and progression through the G1/S and G2/M checkpoints. In summary, we suggest that H. pylori disrupts expression of cell cycle-associated genes, thereby impeding proliferation of RAW264.7 cells, and such disruption may be an immunoevasive strategy utilized by H. pylori.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Low multiplicity of infection of Helicobacter pylori suppresses apoptosis of B lymphocytes.Cancer Res. 2006 Jul 1;66(13):6834-42. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4197. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16818661
-
Helicobacter pylori and mitogen-activated protein kinases regulate the cell cycle, proliferation and apoptosis in gastric epithelial cells.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008 Jul;23(7 Pt 2):e67-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2007.04912.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008. PMID: 18702686
-
Helicobacter pylori attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production by murine macrophages.Innate Immun. 2012 Jun;18(3):406-17. doi: 10.1177/1753425911413164. Epub 2011 Sep 16. Innate Immun. 2012. PMID: 21926162
-
Expression of cdc2 and cyclin B1 in Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric MALT and MALT lymphoma : relationship to cell death, proliferation, and transformation.Am J Pathol. 2000 Jan;156(1):217-25. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64722-0. Am J Pathol. 2000. PMID: 10623670 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon gamma-signature transcript profiling and IL-23 upregulation in response to Helicobacter pylori infection.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2008 Jul-Sep;21(3):515-26. doi: 10.1177/039463200802100305. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18831919
Cited by
-
Regulation of Epigenetic Modifiers, Including KDM6B, by Interferon-γ and Interleukin-4 in Human Macrophages.Front Immunol. 2017 Feb 8;8:92. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00092. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28228757 Free PMC article.
-
Innate Immunity Crosstalk with Helicobacter pylori: Pattern Recognition Receptors and Cellular Responses.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 8;23(14):7561. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147561. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35886908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Transcription Study of Cryptococcus neoformans H99 Clinical Strain versus Environmental Strains.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 11;10(9):e0137457. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137457. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26360021 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear carbonic anhydrase 6B associates with PRMT5 to epigenetically promote IL-12 expression in innate response.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Aug 8;114(32):8620-8625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1700917114. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28739930 Free PMC article.
-
Podoplanin Drives Motility of Active Macrophage via Regulating Filamin C During Helicobacter pylori Infection.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 11;12:702156. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.702156. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34707599 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pathak S. K., Tavares R., de Klerk N., Spetz A. L. & Jonsson A. B. Helicobacter pylori protein JHP0290 binds to multiple cell types and induces macrophage apoptosis via tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-dependent and independent pathways. PloS one 8, e77872, 10.1371/journal.pone.0077872 (2013). - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

