Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis: A Potential Complication of Treatment With Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibition
- PMID: 26078479
- PMCID: PMC4542270
- DOI: 10.2337/dc15-0843
Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis: A Potential Complication of Treatment With Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibition
Abstract
Objective: Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors are the most recently approved antihyperglycemic medications. We sought to describe their association with euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis (euDKA) in hopes that it will enhance recognition of this potentially life-threatening complication.
Research design and methods: Cases identified incidentally are described.
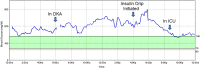
Results: We identified 13 episodes of SGLT-2 inhibitor-associated euDKA or ketosis in nine individuals, seven with type 1 diabetes and two with type 2 diabetes, from various practices across the U.S. The absence of significant hyperglycemia in these patients delayed recognition of the emergent nature of the problem by patients and providers.
Conclusions: SGLT-2 inhibitors seem to be associated with euglycemic DKA and ketosis, perhaps as a consequence of their noninsulin-dependent glucose clearance, hyperglucagonemia, and volume depletion. Patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes who experience nausea, vomiting, or malaise or develop a metabolic acidosis in the setting of SGLT-2 inhibitor therapy should be promptly evaluated for the presence of urine and/or serum ketones. SGLT-2 inhibitors should only be used with great caution, extensive counseling, and close monitoring in the setting of type 1 diabetes.
© 2015 by the American Diabetes Association. Readers may use this article as long as the work is properly cited, the use is educational and not for profit, and the work is not altered.
Figures
Comment in
-
Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis: A Predictable, Detectable, and Preventable Safety Concern With SGLT2 Inhibitors.Diabetes Care. 2015 Sep;38(9):1638-42. doi: 10.2337/dc15-1380. Diabetes Care. 2015. PMID: 26294774 No abstract available.
-
Canagliflozin use in Type I diabetes mellitus.Postgrad Med. 2017 Apr;129(3):336-339. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2017.1264855. Epub 2016 Dec 5. Postgrad Med. 2017. PMID: 27918226
References
-
- Tahrani AA, Bailey CJ, Del Prato S, Barnett AH. Management of type 2 diabetes: new and future developments in treatment. Lancet 2011;378:182–197 - PubMed
-
- Henry RR, Rosenstock J, Edelman S, et al. . Exploring the potential of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin in type 1 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Diabetes Care 2015;38:412–419 - PubMed
-
- Lamos EM, Younk LM, Davis SN. Empagliflozin, a sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor, in the treatment of type 1 diabetes. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2014;23:875–882 - PubMed
-
- Perkins BA, Cherney DZ, Partridge H, et al. . Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition and glycemic control in type 1 diabetes: results of an 8-week open-label proof-of-concept trial. Diabetes Care 2014;37:1480–1483 - PubMed
-
- Cherney DZI, Perkins BA, Soleymanlou N, et al. . Renal hemodynamic effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Circulation 2014;129:587–597 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical