Platycodin-D Induced Autophagy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells via PI3K/Akt/mTOR and MAPK Signaling Pathways
- PMID: 26078792
- PMCID: PMC4466411
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.11291
Platycodin-D Induced Autophagy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells via PI3K/Akt/mTOR and MAPK Signaling Pathways
Abstract
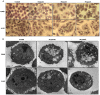
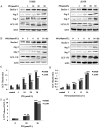
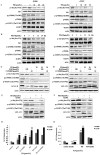
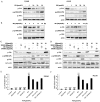
Platycodin-D (PD) is an effective triterpene saponin extracted from the root of Platycodon grandiflorum which has been used clinically to treat pulmonary diseases in traditional Chinese medicine. Recently, it has been reported that PD has anti-tumor effects in various cancer models through the induction of apoptosis. However, whether PD induces autophagy in both cell lines and its molecular mechanisms have not been elucidated. Here, our present study confirmed that PD induced autophagy in both NCI-H460 and A549 cells via up-regulating the expression levels of Atg-3, Atg-7 and Beclin-1. Meanwhile, PD contributed to the up-regulation of LC3-II at both protein and mRNA levels. Further detection of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway compared to LY294002 (PI3K kinase inhibitor), RAP (mTOR kinase inhibitor) and insulin (an activator of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway) showed that PD induced autophagy through inhibiting the pathway at p-Akt (Ser473), p-p70S6K (Thr389) and p-4EBP1 (Thr37/46) in both cell lines. Moreover, the examination of MAPK signaling pathway showed that PD treatment increased the phosphorylation of JNK and p38 MAPK, while decreased the phosphorylation of Erk1/2 in both cell lines. Additionally, the effects assessed with a panel of pharmacologic inhibitors, including U0126 (Erk1/2 kinase inhibitor), SP600125 (JNK kinase inhibitor) and SB203580 (p38 MAPK kinase inhibitor) suggested that the activation of JNK and p38 MAPK participated in PD-induced autophagy. Taken together, these findings suggested that PD induced autophagy in NCI-H460 and A549 cells through inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and activating JNK and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Therefore, PD may be an alternative compound for NSCLC therapy.
Keywords: MAPK signaling pathways; PI3K/Akt/mTOR; Platycodin-D; autophagy; non-small cell lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Chun J, Joo EJ, Kang M. et al. Platycodin D induces anoikis and caspase-mediated apoptosis via p38 MAPK in AGS human gastric cancer cells. Journal of cellular biochemistry. 2013;114(2):456–470. - PubMed
-
- Yu JS, Kim AK. Platycodin D induces apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Journal of medicinal food. 2010;13(2):298–305. - PubMed
-
- Kim MO, Moon DO, Choi YH. et al. Platycodin D induces mitotic arrest in vitro, leading to endoreduplication, inhibition of proliferation and apoptosis in leukemia cells. International journal of cancer Journal international du cancer. 2008;122(12):2674–2681. - PubMed
-
- Janku F, McConkey DJ, Hong DS. et al. Autophagy as a target for anticancer therapy. Nature reviews Clinical oncology. 2011;8(9):528–539. - PubMed
-
- Chen S, Rehman SK, Zhang W. et al. Autophagy is a therapeutic target in anticancer drug resistance. Biochimica et biophysica acta. 2010;1806(2):220–229. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

