Combined deletion of p38γ and p38δ reduces skin inflammation and protects from carcinogenesis
- PMID: 26079427
- PMCID: PMC4536989
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4320
Combined deletion of p38γ and p38δ reduces skin inflammation and protects from carcinogenesis
Abstract
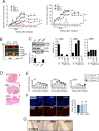
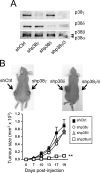
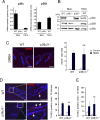
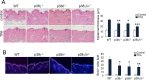
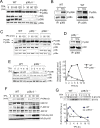
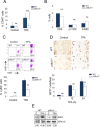
The contribution of chronic skin inflammation to the development of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is poorly understood. While the mitogen-activated protein kinase p38α regulates inflammatory responses and tumour development, little is known about the role of p38γ and p38δ in these processes. Here we show that combined p38γ and p38δ (p38γ/δ) deletion blocked skin tumour development in a chemically induced carcinogenesis model. p38γ/δ deletion reduced TPA-induced epidermal hyperproliferation and inflammation; it inhibited expression of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in keratinocytes in vitro and in whole skin in vivo, resulting in decreased neutrophil recruitment to skin. Our data indicate that p38γ/δ in keratinocytes promote carcinogenesis by enabling formation of a proinflammatory microenvironment that fosters epidermal hyperproliferation and tumourigenesis. These findings provide genetic evidence that p38γ and p38δ have essential roles in skin tumour development, and suggest that targeting inflammation through p38γ/δ offers a therapeutic strategy for SCC treatment and prevention.
Keywords: inflammation-associated cancer; knockout mice; p38γ; p38δ; skin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clinicopathological significance of p38β, p38γ, and p38δ and its biological roles in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jun;37(6):7255-66. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4610-9. Epub 2015 Dec 14. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26666822
-
Pro-oncogenic role of alternative p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases p38γ and p38δ, linking inflammation and cancer in colitis-associated colon cancer.Cancer Res. 2014 Nov 1;74(21):6150-60. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0870. Epub 2014 Sep 12. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25217523
-
Alternative p38 MAPKs are essential for collagen-induced arthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014 May;66(5):1208-17. doi: 10.1002/art.38327. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 24782184
-
P38 kinase in gastrointestinal cancers.Cancer Gene Ther. 2023 Sep;30(9):1181-1189. doi: 10.1038/s41417-023-00622-1. Epub 2023 May 29. Cancer Gene Ther. 2023. PMID: 37248432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p38γ and p38δ Mitogen Activated Protein Kinases (MAPKs), New Stars in the MAPK Galaxy.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016 Apr 14;4:31. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2016.00031. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27148533 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Title: p38δ Regulates IL6 Expression Modulating ERK Phosphorylation in Preadipocytes.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jan 17;9:708844. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.708844. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35111744 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of p38γ in Cancer: From review to outlook.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Sep 23;17(14):4036-4046. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.63537. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34671218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p38γ and p38δ Are Involved in T Lymphocyte Development.Front Immunol. 2018 Jan 29;9:65. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00065. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29434594 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of p38γ attenuates ethanol consumption- and acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice through promoting Dlg1.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022 Jul;43(7):1733-1748. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00795-1. Epub 2021 Nov 17. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022. PMID: 34789918 Free PMC article.
-
Deregulation of the pRb-E2F4 axis alters epidermal homeostasis and favors tumor development.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 15;7(46):75712-75728. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12362. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27708231 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brantsch K.D., Meisner C., Schonfisch B., Trilling B., Wehner-Caroli J., Rocken M., Breuninger H. Analysis of risk factors determining prognosis of cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma: a prospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2008;9:713–720. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Zuazaga J., Olbricht S.M. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Adv Dermatol. 2008;24:33–57. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D., Coussens L.M. Accessories to the crime: functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 2012;21:309–322. - PubMed
-
- Baldursson B., Sigurgeirsson B., Lindelof B. Leg ulcers and squamous cell carcinoma. An epidemiological study and a review of the literature. Acta Derm Venereol. 1993;73:171–174. - PubMed
-
- Motswaledi M.H., Doman C. Lupus vulgaris with squamous cell carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34:939–941. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

