Vitamin D in Primary Hyperparathyroidism: Effects on Clinical, Biochemical, and Densitometric Presentation
- PMID: 26079779
- PMCID: PMC4570160
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2015-2022
Vitamin D in Primary Hyperparathyroidism: Effects on Clinical, Biochemical, and Densitometric Presentation
Abstract
Context: Vitamin D (25-hydroxyvitamin D [25OHD]) deficiency (<20 ng/mL) and insufficiency (20-29 ng/mL) are common in primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT), but data regarding their skeletal effects in PHPT are limited.
Objective: The objective was to evaluate the association between 25OHD levels and PHPT severity.
Design, settings, and participants: This is a cross-sectional analysis of 100 PHPT patients with and without 25OHD insufficiency and deficiency from a university hospital setting.
Outcome measures: We measured calciotropic hormones, bone turnover markers, and bone mineral density (BMD) by dual x-ray absorptiometry.
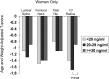
Results: Lower 25OHD was associated with some (PTH: r = -0.42; P < .0001; 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D: r = -0.27; P = .008; serum PO4: r = 0.31; P = .002) but not all (serum/urine calcium) indicators of PHPT severity. Lower 25OHD was also associated with younger age, higher body mass index, male gender, better renal function, and lower vitamin D intake. Comparison of those with deficient (<20 ng/mL; 19%) vs insufficient (20-29 ng/mL; 35%) vs replete (≥30 ng/mL; 46%) 25OHD demonstrated more severe PHPT as reflected by higher PTH (mean ± SEM, 126 ± 10 vs 81 ± 7 vs 72 ± 7 pg/mL; P < .0001) but no difference in nephrolithiasis, osteoporosis, fractures, serum or urinary calcium, bone turnover markers, or BMD after adjustment for age and weight. In women, T-scores at the 1/3 radius were lower in those with 25OHD of 20-29 ng/mL, compared to those who were vitamin D replete (P = .048). In multiple regression modeling, 25OHD (but not PTH) was an independent predictor of 1/3 radius BMD.
Conclusion: Vitamin D deficiency is associated with more severe PHPT as reflected by PTH levels, but effects on BMD are limited to the cortical 1/3 radius and are quite modest. These data support international guidelines that consider PHPT patients with 25OHD <20 ng/mL to be deficient. However, in this cohort with few profoundly vitamin D-deficient patients, vitamin D status did not appear to significantly impact clinical presentation or bone density.
Figures

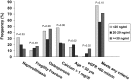
References
-
- Moosgaard B, Vestergaard P, Heickendorff L, Melsen F, Christiansen P, Mosekilde L. Vitamin D status, seasonal variations, parathyroid adenoma weight and bone mineral density in primary hyperparathyroidism. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2005;63:506–513. - PubMed
-
- Boudou P, Ibrahim F, Cormier C, Sarfati E, Souberbielle JC. A very high incidence of low 25 hydroxy-vitamin D serum concentration in a French population of patients with primary hyperparathyroidism. J Endocrinol Invest. 2006;29:511–515. - PubMed
-
- Rao DS, Agarwal G, Talpos GB, et al. Role of vitamin D and calcium nutrition in disease expression and parathyroid tumor growth in primary hyperparathyroidism: a global perspective. J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17(suppl 2):N75–N80. - PubMed
-
- Silverberg SJ, Shane E, Jacobs TP, Siris E, Bilezikian JP. A 10-year prospective study of primary hyperparathyroidism with or without parathyroid surgery. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1249–1255. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

