Perioperative Blood Transfusion Promotes Worse Outcomes of Bladder Cancer after Radical Cystectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 26080092
- PMCID: PMC4469696
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130122
Perioperative Blood Transfusion Promotes Worse Outcomes of Bladder Cancer after Radical Cystectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Multiple studies have investigated the effect of perioperative blood transfusion (PBT) for patients with radical cystectomy (RC), but the results have been inconsistent. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to investigate the relationship between PBT and the clinical outcomes of RC patients.
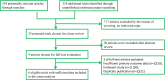
Methods: We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, the Cochrane library and BIOSIS previews to identify relevant literature for studies that focused on the relationship of PBT and outcomes of patients undergoing RC. A fixed or random effects model was used in this meta-analysis to calculate the pooled hazard ratio (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results: A total of 7080 patients in 6 studies matched the selection criteria. Aggregation of the data suggested that PBT in patients who underwent RC correlated with increased all-cause mortality, cancer-specific mortality and cancer recurrence. The combined HRs were 1.19 (n = 6 studies, 95% CI: 1.11-1.27, Z = 4.71, P<0.00001), 1.17 (n = 4 studies, 95% CI: 1.06-1.30, Z = 3.06, P = 0.002), 1.14 (n = 3 studies, 95% CI: 1.03-1.27, Z = 2.50, P = 0.01), respectively. The all-cause mortality associated with PBT did not vary by the characteristics of the study, including number of study participants, follow-up period and the median blood transfusion ratio of the study.
Conclusion: Our data showed that PBT significantly increased the risks of all-cause mortality, cancer-specific mortality and cancer recurrence in patients undergoing RC for bladder cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2011;61(2):69–90. - PubMed
-
- Chang SS, Smith JA Jr., Wells N, Peterson M, Kovach B, Cookson MS. Estimated blood loss and transfusion requirements of radical cystectomy. The Journal of urology. 2001;166(6):2151–4. - PubMed
-
- Douglas T, McLeod D. Modification of the surgical technique in radical cystectomy. Techniques in urology. 1995;2(2):73–6. - PubMed
-
- Nosotti M, Rebulla P, Riccardi D, Baisi A, Bellaviti N, Rosso L, et al. Correlation between perioperative blood transfusion and prognosis of patients subjected to surgery for stage I lung cancer. CHEST Journal. 2003;124(1):102–7. - PubMed
-
- Rzyman W, Dziadziuszko R, Skokowski J, Wilimski R, Raiter A, Szymanowska A, et al. The influence of blood transfusion on survival in operated non–small cell lung cancer patients. The Journal of thoracic and cardiovascular surgery. 2003;126(3):755–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

