Drop-on-Demand System for Manufacturing of Melt-based Solid Oral Dosage: Effect of Critical Process Parameters on Product Quality
- PMID: 26082005
- PMCID: PMC4984897
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-015-0348-3
Drop-on-Demand System for Manufacturing of Melt-based Solid Oral Dosage: Effect of Critical Process Parameters on Product Quality
Abstract
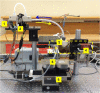
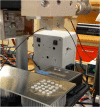
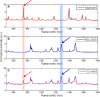
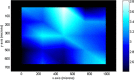
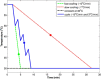
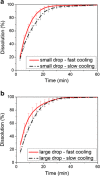
The features of a drop-on-demand-based system developed for the manufacture of melt-based pharmaceuticals have been previously reported. In this paper, a supervisory control system, which is designed to ensure reproducible production of high quality of melt-based solid oral dosages, is presented. This control system enables the production of individual dosage forms with the desired critical quality attributes: amount of active ingredient and drug morphology by monitoring and controlling critical process parameters, such as drop size and product and process temperatures. The effects of these process parameters on the final product quality are investigated, and the properties of the produced dosage forms characterized using various techniques, such as Raman spectroscopy, optical microscopy, and dissolution testing. A crystallization temperature control strategy, including controlled temperature cycles, is presented to tailor the crystallization behavior of drug deposits and to achieve consistent drug morphology. This control strategy can be used to achieve the desired bioavailability of the drug by mitigating variations in the dissolution profiles. The supervisor control strategy enables the application of the drop-on-demand system to the production of individualized dosage required for personalized drug regimens.
Keywords: critical process parameters; critical quality attributes; drop-on-demand; drug printing; supervisory control.
Figures




References
-
- Gupta A, Giridhar A, Venkatasubramanian V, Reklaitis GV. Intelligent alarm management applied to continuous pharmaceutical tablet manufacturing: an integrated approach. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2013;52(35):12357–68. doi: 10.1021/ie3035042. - DOI
-
- Food and Drug Administration CDER. Guidance for industry PAT—a framework for innovative pharmaceutical. 2004.
-
- Simon LL, Pataki H, Marosi G, Meemken F, Hungerbu K, Baiker A, et al. Assessment of recent process analytical technology (PAT) trends: a multiauthor review. Org Process Res Dev. 2015;19(1):3–62. doi: 10.1021/op500261y. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

