Selective neuronal vulnerability of human hippocampal CA1 neurons: lesion evolution, temporal course, and pattern of hippocampal damage in diffusion-weighted MR imaging
- PMID: 26082014
- PMCID: PMC4635239
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2015.137
Selective neuronal vulnerability of human hippocampal CA1 neurons: lesion evolution, temporal course, and pattern of hippocampal damage in diffusion-weighted MR imaging
Abstract
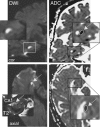
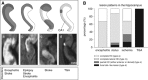
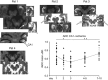
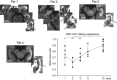
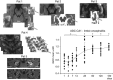
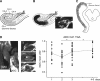
The CA1 (cornu ammonis) region of hippocampus is selectively vulnerable to a variety of metabolic and cytotoxic insults, which is mirrored in a delayed neuronal death of CA1 neurons. The basis and mechanisms of this regional susceptibility of CA1 neurons are poorly understood, and the correlates in human diseases affecting the hippocampus are not clear. Adopting a translational approach, the lesion evolution, temporal course, pattern of diffusion changes, and damage in hippocampal CA1 in acute neurologic disorders were studied using high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. In patients with hippocampal ischemia (n=50), limbic encephalitis (n=30), after status epilepticus (n=17), and transient global amnesia (n=53), the CA1 region was selectively affected compared with other CA regions of the hippocampus. CA1 neurons exhibited a maximum decrease of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) 48 to 72 hours after the insult, irrespective of the nature of the insult. Hypoxic-ischemic insults led to a significant lower ADC suggesting that the ischemic insult results in a stronger impairment of cellular metabolism. The evolution of diffusion changes show that CA1 diffusion lesions mirror the delayed time course of the pathophysiologic cascade typically observed in animal models. Studying the imaging correlates of hippocampal damage in humans provides valuable insight into the pathophysiology and neurobiology of the hippocampus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Focal lesions of human hippocampal CA1 neurons in transient global amnesia impair place memory.Science. 2010 Jun 11;328(5984):1412-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1188160. Science. 2010. PMID: 20538952
-
Selective affection of hippocampal CA-1 neurons in patients with transient global amnesia without long-term sequelae.Brain. 2006 Nov;129(Pt 11):2874-84. doi: 10.1093/brain/awl248. Epub 2006 Sep 26. Brain. 2006. PMID: 17003071
-
Evolution of hippocampal CA-1 diffusion lesions in transient global amnesia.Ann Neurol. 2007 Nov;62(5):475-80. doi: 10.1002/ana.21189. Ann Neurol. 2007. PMID: 17702037
-
Genomic approach to selective vulnerability of the hippocampus in brain ischemia-hypoxia.Neuroscience. 2015 Nov 19;309:259-79. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.08.034. Epub 2015 Sep 14. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 26383255 Review.
-
Hippocampal modifications in transient global amnesia.Rev Neurol (Paris). 2015 Mar;171(3):282-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neurol.2015.01.003. Epub 2015 Mar 11. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2015. PMID: 25769554 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia/Ischemia-Induced Rod Microglia Phenotype in CA1 Hippocampal Slices.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 26;23(3):1422. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031422. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163344 Free PMC article.
-
Different Patterns of Neurodegeneration and Glia Activation in CA1 and CA3 Hippocampal Regions of TgCRND8 Mice.Front Aging Neurosci. 2018 Nov 13;10:372. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00372. eCollection 2018. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30483118 Free PMC article.
-
Phenomic Microglia Diversity as a Druggable Target in the Hippocampus in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 5;24(18):13668. doi: 10.3390/ijms241813668. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37761971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transdiagnostic hippocampal damage patterns in neuroimmunological disorders.Neuroimage Clin. 2020;28:102515. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102515. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Neuroimage Clin. 2020. PMID: 33396002 Free PMC article.
-
Innovative in vivo rat model for global cerebral hypoxia: a new approach to investigate therapeutic and preventive drugs.Front Physiol. 2024 Feb 9;15:1293247. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1293247. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38405120 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 1Schmidt-Kastner R, Freund TF. Selective vulnerability of the hippocampus in brain ischemia. Neuroscience 1991; 40: 599–636. - PubMed
-
- 2Kirino T. Delayed neuronal death. Neuropathology 2000; 20: S95–S97. - PubMed
-
- 3Kirino T. Delayed neuronal death in the gerbil hippocampus following ischemia. Brain Res 1982; 239: 57–69. - PubMed
-
- 4Pulsinelli WA, Brierley JB, Plum F. Temporal profile of neuronal damage in a model of transient forebrain ischemia. Ann Neurol 1982; 11: 491–498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

