A prospective comparison of alginate-hydrogel with standard medical therapy to determine impact on functional capacity and clinical outcomes in patients with advanced heart failure (AUGMENT-HF trial)
- PMID: 26082085
- PMCID: PMC4561351
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv259
A prospective comparison of alginate-hydrogel with standard medical therapy to determine impact on functional capacity and clinical outcomes in patients with advanced heart failure (AUGMENT-HF trial)
Abstract
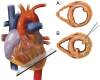
Aims: AUGMENT-HF was an international, multi-centre, prospective, randomized, controlled trial to evaluate the benefits and safety of a novel method of left ventricular (LV) modification with alginate-hydrogel.
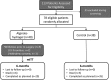
Methods: Alginate-hydrogel is an inert permanent implant that is directly injected into LV heart muscle and serves as a prosthetic scaffold to modify the shape and size of the dilated LV. Patients with advanced chronic heart failure (HF) were randomized (1 : 1) to alginate-hydrogel (n = 40) in combination with standard medical therapy or standard medical therapy alone (Control, n = 38). The primary endpoint of AUGMENT-HF was the change in peak VO2 from baseline to 6 months. Secondary endpoints included changes in 6-min walk test (6MWT) distance and New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class, as well as assessments of procedural safety.
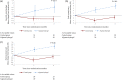
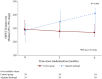
Results: Enrolled patients were 63 ± 10 years old, 74% in NYHA functional class III, had a LV ejection fraction of 26 ± 5% and a mean peak VO2 of 12.2 ± 1.8 mL/kg/min. Thirty-five patients were successfully treated with alginate-hydrogel injections through a limited left thoracotomy approach without device-related complications; the 30-day surgical mortality was 8.6% (3 deaths). Alginate-hydrogel treatment was associated with improved peak VO2 at 6 months-treatment effect vs.
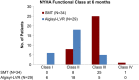
Control: +1.24 mL/kg/min (95% confidence interval 0.26-2.23, P = 0.014). Also 6MWT distance and NYHA functional class improved in alginate-hydrogel-treated patients vs. Control (both P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Alginate-hydrogel in addition to standard medical therapy for patients with advanced chronic HF was more effective than standard medical therapy alone for improving exercise capacity and symptoms. The results of AUGMENT-HF provide proof of concept for a pivotal trial.
Trial registration number: NCT01311791.
Keywords: Advanced chronic heart failure; Alginate-hydrogel; Exercise capacity; Safety; Symptoms.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Augmenting outcomes in patients with advanced heart failure.Eur Heart J. 2015 Sep 7;36(34):2276-8. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv283. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Eur Heart J. 2015. PMID: 26093637 No abstract available.
-
Heart failure: Alginate-hydrogel in chronic HF.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015 Aug;12(8):443. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2015.107. Epub 2015 Jul 7. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 26149488 No abstract available.
References
-
- Mihardja SS, Gonzales JA, Gao D, Sievers RE, Fang Q, Stillson CA, Yu J, Peng M, Lee RJ. The effect of a peptide-modified thermo-reversible methylcellulose on wound healing and LV function in a chronic myocardial infarction rodent model. Biomaterials 2013;34:8869–8877. - PubMed
-
- Song M, Jang H, Lee J, Kim JH, Kim SH, Sun K, Park Y. Regeneration of chronic myocardial infarction by injectable hydrogels containing stem cell homing factor SDF-1 and angiogenic peptide Ac-SDKP. Biomaterials 2014;35:2436–2445. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

