Predictors of placebo response in peripheral neuropathic pain: insights from pregabalin clinical trials
- PMID: 26082659
- PMCID: PMC4459620
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S78303
Predictors of placebo response in peripheral neuropathic pain: insights from pregabalin clinical trials
Abstract
Background: Greater understanding of factors associated with the high placebo-response rates noted in recent neuropathic pain trials may improve trial design. This study investigated placebo response and its predictors in pregabalin trials in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) or postherpetic neuralgia.
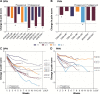
Patients and methods: Individual patient data from 16 randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trials of pregabalin in 3,053 patients with DPN and 1,460 patients with postherpetic neuralgia were pooled (by condition and all together) in order to investigate the placebo response and its predictors. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed across all 16 trials to identify predictors of change in pain score in patients. Trials with a >2-point mean reduction in pain score at endpoint with placebo were designated high placebo response and were compared with low placebo-response trials (those with a ≤2-point mean reduction) with respect to patient and study characteristics.
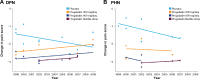
Results: Three high placebo-response studies were identified, with all in DPN patients and all conducted postapproval of pregabalin. Younger age, higher mean baseline pain score, longer study duration, higher ratio of patients on active treatment to placebo, and study conducted postapproval were all significantly associated with a higher placebo response (P<0.05). There was a trend towards an increased placebo response in all studies over time without any corresponding change in the response to pregabalin.
Conclusion: Consideration of the factors identified here as contributing to a higher placebo response could help improve the sensitivity and accuracy of clinical trials in patients with neuropathic pain.
Keywords: diabetic peripheral neuropathy; postherpetic neuralgia.
Figures
References
-
- Dworkin RH, Turk DC, Peirce-Sandner S, et al. Placebo and treatment group responses in postherpetic neuralgia vs. painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy clinical trials in the REPORT database. Pain. 2010;150(1):12–16. - PubMed
-
- Thienel U, Neto W, Schwabe SK, Vijapurkar U, Topiramate Diabetic Neuropathic Pain Study Group Topiramate in painful diabetic polyneuropathy: findings from three double-blind placebo-controlled trials. Acta Neurol Scand. 2004;110(4):221–231. - PubMed
-
- Silver M, Blum D, Grainger J, Hammer AE, Quessy S. Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of lamotrigine in combination with other medications for neuropathic pain. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2007;34(4):446–454. - PubMed
-
- Vinik AI, Tuchman M, Safirstein B, et al. Lamotrigine for treatment of pain associated with diabetic neuropathy: results of two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies. Pain. 2007;128(1–2):169–179. - PubMed
-
- Häuser W, Bartram-Wunn E, Bartram C, Reinecke H, Tölle T. Systematic review: Placebo response in drug trials of fibromyalgia syndrome and painful peripheral diabetic neuropathy-magnitude and patient-related predictors. Pain. 2011;152(8):1709–1717. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

