Efficacy of Lapatinib in Therapy-Resistant HER2-Positive Circulating Tumor Cells in Metastatic Breast Cancer
- PMID: 26083256
- PMCID: PMC4471111
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123683
Efficacy of Lapatinib in Therapy-Resistant HER2-Positive Circulating Tumor Cells in Metastatic Breast Cancer
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the efficacy of lapatinib, a dual EGFR and HER2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in therapy-resistant HER2-positive CTCs in metastatic breast cancer (MBC).
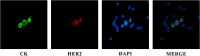
Patients and methods: Patients with MBC and HER2-positive CTCs despite disease stabilization or response to prior therapy, received lapatinib 1500 mg daily in monthly cycles, till disease progression or CTC increase. CTC monitoring was performed by immunofluorescent microscopy using cytospins of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) double stained for HER2 or EGFR and cytokeratin.
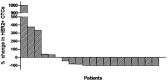
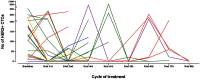
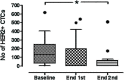
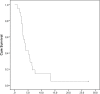
Results: A total of 120 cycles were administered in 22 patients; median age was 62.5 years, 15 (68.2%) patients were post-menopausal and 20 (90.1%) had HER2-negative primary tumors. At the end of the second course, HER2-positive CTC counts decreased in 76.2% of patients; the median number of HER2-positive CTCs/patient also declined significantly (p = 0.013), however the decrease was significant only among patients presenting disease stabilization (p = 0.018) but not among those with disease progression during lapatinib treatment. No objective responses were observed. All CTC-positive patients harbored EGFR-positive CTCs on progression compared to 62.5% at baseline (p = 0.054). The ratio of EGFR-positive CTCs/total CTCs detected in all patients increased from 17.1% at baseline to 37.6% on progression, whereas the mean percentage of HER2-negative CTCs/patient increased from 2.4% to 30.6% (p = 0.03).
Conclusions: The above results indicate that lapatinib is effective in decreasing HER2-positive CTCs in patients with MBC irrespectively of the HER2 status of the primary tumor and imply the feasibility of monitoring the molecular changes on CTCs during treatment with targeted agents.
Trial registration: Clinical trial.gov NCT00694252.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Braun S, Vogl FD, Naume B, Janni W, Osborne MP, et al. (2005) A pooled analysis of bone marrow micrometastasis in breast cancer. N Engl J Med 353: 793–802. - PubMed
-
- Stathopoulou A, Vlachonikolis I, Mavroudis D, Perraki M, Kouroussis C, et al. (2002) Molecular detection of cytokeratin-19-positive cells in the peripheral blood of patients with operable breast cancer: evaluation of their prognostic significance. J Clin Oncol 20: 3404–3412. - PubMed
-
- Xenidis N, Perraki M, Kafousi M, Apostolaki S, Bolonaki I, et al. (2006) Predictive and prognostic value of peripheral blood cytokeratin-19 mRNA-positive cells detected by real-time polymerase chain reaction in node-negative breast cancer patients. J Clin Oncol 24: 3756–3762. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

