Small-Molecule-Mediated Degradation of the Androgen Receptor through Hydrophobic Tagging
- PMID: 26083457
- PMCID: PMC4547777
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201503720
Small-Molecule-Mediated Degradation of the Androgen Receptor through Hydrophobic Tagging
Abstract
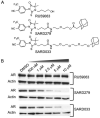
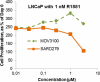
Androgen receptor (AR)-dependent transcription is a major driver of prostate tumor cell proliferation. Consequently, it is the target of several antitumor chemotherapeutic agents, including the AR antagonist MDV3100/enzalutamide. Recent studies have shown that a single AR mutation (F876L) converts MDV3100 action from an antagonist to an agonist. Here we describe the generation of a novel class of selective androgen receptor degraders (SARDs) to address this resistance mechanism. Molecules containing hydrophobic degrons linked to small-molecule AR ligands induce AR degradation, reduce expression of AR target genes and inhibit proliferation in androgen-dependent prostate cancer cell lines. These results suggest that selective AR degradation may be an effective therapeutic prostate tumor strategy in the context of AR mutations that confer resistance to second-generation AR antagonists.
Keywords: antiproliferation; cancer; drug design; hormones; protein degradation.
© 2015 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures


References
-
- Kim DH, Rossi JJ. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:173–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

