Genome-wide association study of acute kidney injury after coronary bypass graft surgery identifies susceptibility loci
- PMID: 26083657
- PMCID: PMC4589439
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2015.161
Genome-wide association study of acute kidney injury after coronary bypass graft surgery identifies susceptibility loci
Abstract
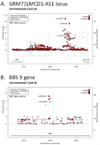
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common, serious complication of cardiac surgery. Since prior studies have supported a genetic basis for postoperative AKI, we conducted a genome-wide association study (GWAS) for AKI following coronary bypass graft (CABG) surgery. The discovery data set consisted of 873 nonemergent CABG surgery patients with cardiopulmonary bypass (PEGASUS), while a replication data set had 380 cardiac surgical patients (CATHGEN). Single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) data were based on Illumina Human610-Quad (PEGASUS) and OMNI1-Quad (CATHGEN) BeadChips. We used linear regression with adjustment for a clinical AKI risk score to test SNP associations with the postoperative peak rise relative to preoperative serum creatinine concentration as a quantitative AKI trait. Nine SNPs meeting significance in the discovery set were detected. The rs13317787 in GRM7|LMCD1-AS1 intergenic region (3p21.6) and rs10262995 in BBS9 (7p14.3) were replicated with significance in the CATHGEN data set and exhibited significantly strong overall association following meta-analysis. Additional fine mapping using imputed SNPs across these two regions and meta-analysis found genome-wide significance at the GRM7|LMCD1-AS1 locus and a significantly strong association at BBS9. Thus, through an unbiased GWAS approach, we found two new loci associated with post-CABG AKI providing new insights into the pathogenesis of perioperative AKI.
Figures

References
-
- Carmichael P, Carmichael AR. Acute renal failure in the surgical setting. ANZ J Surg. 2003;73:144–153. - PubMed
-
- Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, et al. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. Jama. 2005;294:813–818. - PubMed
-
- Loef BG, Epema AH, Smilde TD, et al. Immediate postoperative renal function deterioration in cardiac surgical patients predicts in-hospital mortality and long-term survival. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:195–200. - PubMed
-
- Swaminathan M, Hudson CC, Phillips-Bute BG, et al. Impact of early renal recovery on survival after cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury. Ann Thorac Surg. 2010;89:1098–1104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL092071/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL108280/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-30/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HL075273/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL109971/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL054316/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL095987/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL075273/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL096978/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG016762/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL069081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL101621/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL095987/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL069081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL096978/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000030/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL101621/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG09663/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092071/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL108280/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL109971/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

