Compensatory induction of MYC expression by sustained CDK9 inhibition via a BRD4-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 26083714
- PMCID: PMC4490784
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.06535
Compensatory induction of MYC expression by sustained CDK9 inhibition via a BRD4-dependent mechanism
Erratum in
-
Correction: Compensatory induction of MYC expression by sustained CDK9 inhibition via a BRD4-dependent mechanism.Elife. 2015 Jul 17;4:e09993. doi: 10.7554/eLife.09993. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26186095 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
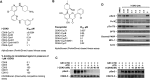
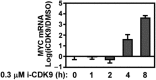
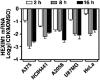
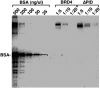
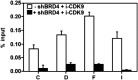
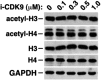
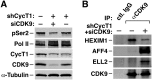
CDK9 is the kinase subunit of positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) that enables RNA polymerase (Pol) II's transition from promoter-proximal pausing to productive elongation. Although considerable interest exists in CDK9 as a therapeutic target, little progress has been made due to lack of highly selective inhibitors. Here, we describe the development of i-CDK9 as such an inhibitor that potently suppresses CDK9 phosphorylation of substrates and causes genome-wide Pol II pausing. While most genes experience reduced expression, MYC and other primary response genes increase expression upon sustained i-CDK9 treatment. Essential for this increase, the bromodomain protein BRD4 captures P-TEFb from 7SK snRNP to deliver to target genes and also enhances CDK9's activity and resistance to inhibition. Because the i-CDK9-induced MYC expression and binding to P-TEFb compensate for P-TEFb's loss of activity, only simultaneously inhibiting CDK9 and MYC/BRD4 can efficiently induce growth arrest and apoptosis of cancer cells, suggesting the potential of a combinatorial treatment strategy.
Keywords: BRD4; CDK9; CDK9 inhibitor; MYC; RNA polymerase pause and release; biochemistry; chromosomes; genes; human; transcriptional elongation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures













References
-
- Bartholomeeusen K, Xiang Y, Fujinaga K, Peterlin BM. Bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) bromodomain inhibition activate transcription via transient release of positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) from 7SK small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2012;287:36609–36616. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.410746. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

