Upregulation of miR-107 Inhibits Glioma Angiogenesis and VEGF Expression
- PMID: 26084601
- PMCID: PMC11482415
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-015-0225-3
Upregulation of miR-107 Inhibits Glioma Angiogenesis and VEGF Expression
Erratum in
-
Correction: Upregulation of miR-107 Inhibits Glioma Angiogenesis and VEGF Expression.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Sep 18;44(1):61. doi: 10.1007/s10571-024-01495-0. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39292316 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
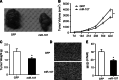
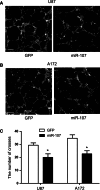
MicroRNAs can function as oncogenes or tumor suppressors in glioma. Previously, we showed that miR-107 inhibits glioma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Since tumor growth and invasion are closely related to angiogenesis, we further examined the role of miR-107 in glioma angiogenesis. In a co-culture of glioma cells and human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMVEC), overexpression of miR-107 in glioma cells led to the inhibition of HBMVEC proliferation, migration, and tube formation ability. ELISA, RT-PCR, and western blot assays revealed that upregulation of miR-107 in glioma cells inhibits VEGF expression. Our findings collectively support the critical involvement of miR-107 in glioma cell angiogenesis and highlight its potential as a therapeutic target for glioma.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Glioma; HBMVEC; VEGF; miR-107.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest were declared.
Figures


References
-
- Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431:350–355 - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297 - PubMed
-
- Brandes AA, Franceschi E, Gorlia T, Wick W, Jacobs AH, Baumert BG, van den Bent M, Weller M, Stupp R (2012) Appropriate end-points for right results in the age of antiangiogenic agents: future options for phase II trials in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Eur J Cancer 48:896–903 - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Chen XR, Zhang R, Li P, Liu Y, Yan K, Jiang XD (2013a) MicroRNA-107 inhibits glioma cell migration and invasion by modulating Notch2 expression. J Neurooncol 112:59–66 - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Zhang R, Li P, Liu Y, Qin K, Fa ZQ, Liu YJ, Ke YQ, Jiang XD (2013b) P53-induced microRNA-107 inhibits proliferation of glioma cells and down-regulates the expression of CDK6 and Notch-2. Neurosci Lett 534:327–332 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

