Single-motor-unit discharge characteristics in human lumbar multifidus muscle
- PMID: 26084900
- PMCID: PMC4725113
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00010.2014
Single-motor-unit discharge characteristics in human lumbar multifidus muscle
Abstract
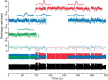
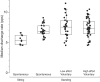
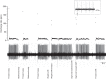
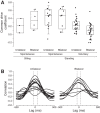
The underlying neurophysiology of postural control of the lower back in humans is poorly understood. We have characterized motor unit (MU) discharge activity in the deep lumbar multifidus (LM) muscle in nine healthy subjects (20-40 yr, 3 females). Bilateral fine wire electrodes were implanted at L4 spinal level using ultrasound guidance. EMG was recorded during spontaneous sitting and standing and during voluntary force production. Individual MUs were analyzed with regard to instantaneous discharge rate, interspike interval variability, alternation of activity between MUs, and cross correlation between concurrently active MUs quantified by the common drive coefficient (CDC). Significant effects of sitting vs. standing were seen on median discharge rate and interspike interval variability. Median discharge rate in 71 units was 5.4 and 6.9 pulses/s during spontaneous sitting and standing and 7.4 pulses/s during voluntary force production. Several MUs fired doublets. CDC analysis of 87 MU pairs showed a significantly higher common drive in spontaneous than in voluntary activity and significant differences between unilateral and bilateral pairs, although not when spontaneously active in standing. In spite of common drive, MUs were recruited from inactivity to tonic discharge lasting for several minutes without changes in discharge rate in already active MUs, and several instances were documented where activity was rotated between MUs. We argue that this behavior is indicative of self-sustained discharge in LM motoneurons, establishing intrinsic motoneuron properties as a central mechanism for postural control of deep back muscles.
Keywords: back; electromyography; motor activity; motor neurons; muscle tonus.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures



References
-
- Bawa P, Murnaghan C. Motor unit rotation in a variety of human muscles. J Neurophysiol 102: 2265–2272, 2009. - PubMed
-
- Bawa P, Pang MY, Olesen KA, Calancie B. Rotation of motoneurons during prolonged isometric contractions in humans. J Neurophysiol 96: 1135–1140, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Biering-Sørensen F. Physical measurements as risk indicators for low-back trouble over a one-year period. Spine 9: 106–119, 1984. - PubMed
-
- Burke RE, Rudomin P, Zajac FE. Catch property in single mammalian motor units. Science 168: 122–124, 1970. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

