Postactivation depression of the Ia EPSP in motoneurons is reduced in both the G127X SOD1 model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and in aged mice
- PMID: 26084911
- PMCID: PMC4725116
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00745.2014
Postactivation depression of the Ia EPSP in motoneurons is reduced in both the G127X SOD1 model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and in aged mice
Abstract
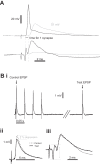
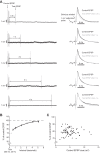
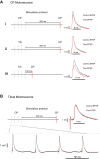
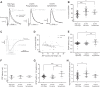
Postactivation depression (PActD) of Ia afferent excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) in spinal motoneurons results in a long-lasting depression of the stretch reflex. This phenomenon (PActD) is of clinical interest as it has been shown to be reduced in a number of spastic disorders. Using in vivo intracellular recordings of Ia EPSPs in adult mice, we demonstrate that PActD in adult (100-220 days old) C57BL/6J mice is both qualitatively and quantitatively similar to that which has been observed in larger animals with respect to both the magnitude (with ∼20% depression of EPSPs at 0.5 ms after a train of stimuli) and the time course (returning to almost normal amplitudes by 5 ms after the train). This validates the use of mouse models to study PActD. Changes in such excitatory inputs to spinal motoneurons may have important implications for hyperreflexia and/or glutamate-induced excitotoxicity in the neurodegenerative disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). With the use of the G127X SOD1 mutant mouse, an ALS model with a prolonged asymptomatic phase and fulminant symptom onset, we observed that PActD is significantly reduced at both presymptomatic (16% depression) and symptomatic (17.3% depression) time points compared with aged-matched controls (22.4% depression). The PActD reduction was not markedly altered by symptom onset. Comparing these PActD changes at the EPSP with the known effect of the depression on the monosynaptic reflex, we conclude that this is likely to have a much larger effect on the reflex itself (a 20-40% difference). Nevertheless, it should also be accounted that in aged (580 day old) C57BL/6J mice there was also a reduction in PActD although, aging is not usually associated with spasticity.
Keywords: ALS; aging; postactivation depression.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Achache V, Roche N, Lamy JC, Boakye M, Lackmy A, Gastal A, Quentin V, Katz R. Transmission within several spinal pathways in adults with cerebral palsy. Brain 133: 1470–1483, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Aymard C, Katz R, Lafitte C, Lo E, Penicaud A, Pradat-Diehl P, Raoul S. Presynaptic inhibition and homosynaptic depression: a comparison between lower and upper limbs in normal human subjects and patients with hemiplegia. Brain 123: 1688–1702, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Bendotti C, Tortarolo M, Suchak SK, Calvaresi N, Carvelli L, Bastone A, Rizzi M, Rattray M, Mennini T. Transgenic SOD1 G93A mice develop reduced GLT-1 in spinal cord without alterations in cerebrospinal fluid glutamate levels. J Neurochem 79: 737–746, 2001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

