Prevalent low-grade dysplasia: the strongest predictor of malignant progression in Barrett's columnar-lined oesophagus
- PMID: 26085438
- PMCID: PMC4752652
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309978
Prevalent low-grade dysplasia: the strongest predictor of malignant progression in Barrett's columnar-lined oesophagus
Keywords: ADENOCARCINOMA; BARRETT'S OESOPHAGUS; DYSPLASIA; OESOPHAGEAL DISORDERS.
Figures
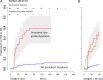
Comment on
-
Barrett's oesophagus patients with low-grade dysplasia can be accurately risk-stratified after histological review by an expert pathology panel.Gut. 2015 May;64(5):700-6. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307278. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Gut. 2015. PMID: 25034523
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
