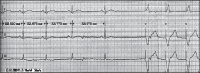
Improved quality of life after treatment of prolonged asystole during breath holding spells with a cardiac pacemaker
- PMID: 26085761
- PMCID: PMC4453178
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-2069.154142
Improved quality of life after treatment of prolonged asystole during breath holding spells with a cardiac pacemaker
Abstract
Objectives: To validate the physical and psychological effectiveness of cardiac pacing in pediatric patients with breath-holding spells (BHS) and prolonged asystole.
Materials and methods: The records and clinical data of all the patients with BHS who presented to our center in the period of 2001-2013 were reviewed. All patients who received cardiac pacemaker implantation for prolonged asystole during BHS were included. In addition, the parents were asked to fill out a standardized quality of life (QOL) questionnaire.
Results: Seven patients were identified. The mean onset of symptoms was 7 month (1-12 months) of age, documented asystole was 12-21 seconds, and a permanent cardiac pacemaker device was implanted at a mean age of 23 months (8 months-3.9 years). No pacemaker related adverse events were recorded. Follow up showed immediate resolution from spells in four cases (4/7). Two patients (2/7) showed significant reduction of frequency and severity of spells, with complete elimination of loss of consciousness (LOC). One patient (1/7) with an additional neurologic disorder continued to have minor pallid BHS and eventually switched from pallid to cyanotic spells without further detection of bradycardia or asystole in holter examination. QOL questionnaire revealed significant reduction in subjective stress levels of patients (P = 0.012) and parents (P = 0.007) after pacemaker implantation.
Conclusion: Cardiac pacing using appropriate pacemaker settings seems effective in the prevention of LOC and reduction of the frequency of BHS. Our results imply a reduction of subjective stress levels of patients and parents as well as an increased quality of everyday life. After all, randomized controlled trials of the influence of cardiac pacemaker implantation on subjective stress levels in patients with BHS are needed.
Keywords: Asystole; breath holding spells; cardiac pacing; children; quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Kelly AM, Porter CJ, McGoon MD, Espinosa RE, Osborn MJ, Hayes DL. Breath holding spells associated with significant bradycardia: Succesful treatment with permanent pacemaker implantation. Pediatrics. 2001;108:698–702. - PubMed
-
- Benbadis S. The differential diagnosis of epilepsy: A critical review. Epilepsy Behav. 2009;15:15–21. - PubMed
-
- Blanc JJ, Corbel C, Mansourati J, Genet L. Evaluation of beta- adrenergic blockader therapy in vasovagal syncope reproduced by head-up tilt test. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 1991;84:1453–7. - PubMed
-
- Breningstall GN. Breath-holding spells. Pediatr Neurol. 1996;14:91–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources