T-cell exhaustion in the tumor microenvironment
- PMID: 26086965
- PMCID: PMC4669840
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2015.162
T-cell exhaustion in the tumor microenvironment
Abstract
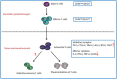
T-cell exhaustion was originally identified during chronic infection in mice, and was subsequently observed in humans with cancer. The exhausted T cells in the tumor microenvironment show overexpressed inhibitory receptors, decreased effector cytokine production and cytolytic activity, leading to the failure of cancer elimination. Restoring exhausted T cells represents an inspiring strategy for cancer treatment, which has yielded promising results and become a significant breakthrough in the cancer immunotherapy. In this review, we overview the updated understanding on the exhausted T cells in cancer and their potential regulatory mechanisms and discuss current therapeutic interventions targeting exhausted T cells in clinical trials.
Figures

References
-
- Kaech SM, Wherry EJ, Ahmed R. Effector and memory T-cell differentiation: implications for vaccine development. Nat Rev Immunol 2002; 2: 251–262. - PubMed
-
- Schluns KS, Lefrancois L. Cytokine control of memory T-cell development and survival. Nat Rev Immunol 2003; 3: 269–279. - PubMed
-
- Baitsch L, Fuertes-Marraco SA, Legat A, Meyer C, Speiser DE. The three main stumbling blocks for anticancer T cells. Trends Immunol 2012; 33: 364–372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

